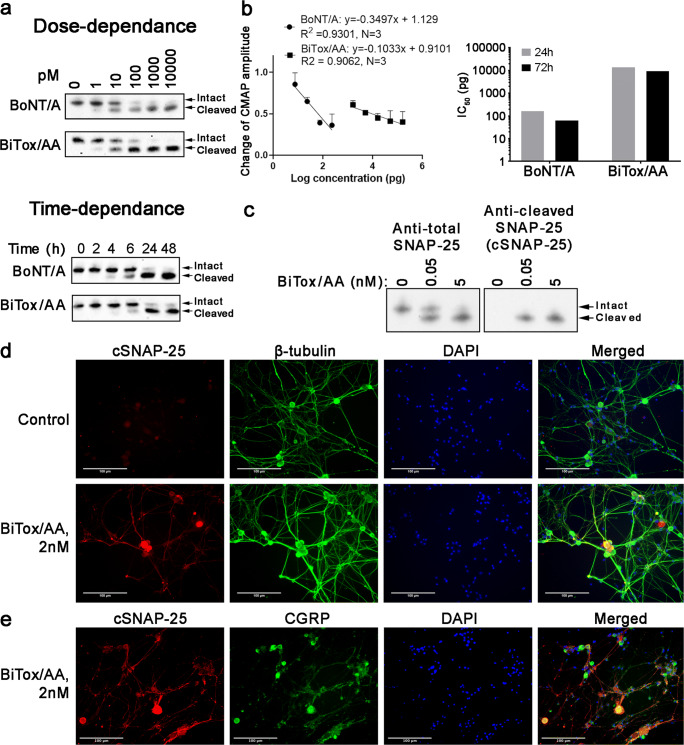
Fig. 2.
Functional evaluation of BiTox/AA in neuronal cultures. (a, Upper panel) example immunoblot of human SiMa neuroblastoma cells treated with BiTox/AA or BoNT/A for 72 h using an anti-SNAP-25 antibody (n = 3). Note the downward molecular shift of SNAP-25 upon the action of botulinum protease correlating with its increasing doses. Positions of the intact and cleaved SNAP-25 are indicated. (a, Lower panel) example immunoblot of SiMa neuroblastoma cells treated with either 1 nM BiTox/AA or 1 nM BoNT/A for the indicated duration of time using an anti-SNAP-25 antibody (n = 3). (b) Graph showing the change in CMAP amplitude measured by EMG in rats 72 h after injection with varying doses of BiTox/AA and BoNT/A, compared to the baseline amplitude (left panel). Bar chart showing the dose difference in logarithmic scale required to achieve 50% reduction in CMAP values measured 24 h and 72 h post injection (right panel). (c) Example immunoblot showing the specificity of the cSNAP-25 antibody to the cleaved end of SNAP-25, as compared to antibody raised against the whole SNAP-25 protein. (d) Examples of fluorescent micrographs of cultured rat trigeminal neurons treated with either vehicle or BiTox/AA and co-immunostained using the cSNAP-25 antibody and an anti-tubulin antibody. (e) BiTox/AA-cleaved SNAP-25 co-localizes with a subset of CGRP neurons in rat trigeminal neuron culture