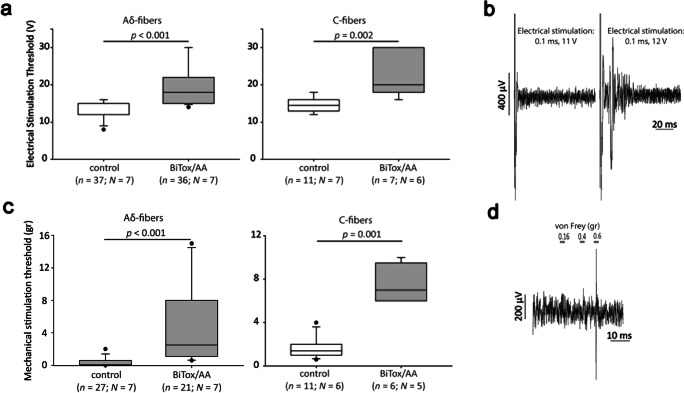
Fig. 4.
Analysis of the inhibitory effect of BiTox/AA on electrical and mechanical activation thresholds of rat primary trigeminal neurons in the trigeminovascular model of migraine. (a) Treatment with BiTox/AA significantly increased the electrical stimulation threshold required to induce an action potential recorded in vivo from trigeminal neurons with Aδ-fiber (p < 0.001, Mann–Whitney U test) and C-fiber (p = 0.002, Mann–Whitney U test) latencies, 7 days post treatment, compared to recordings from trigeminal neurons in animals treated with saline. The whisker plots show the medians with variability outside the upper and lower quartiles. Dots indicate outliers. (b) Examples of traces of post-stimulus recordings with subthreshold (0.1 ms, 11 V) and threshold (0.1 ms, 12 V) electrical stimulations of the periorbital region (assessed as the minimum voltage required to induce evoked action potentials). (c) Treatment with BiTox/AA significantly increased the mechanical stimulation threshold required to induce an action potential recorded in vivo from trigeminal neurons with Aδ- and C-fiber latencies, 7 days post treatment, compared to the mechanical threshold recorded from trigeminal neurons in animals treated with saline. (d) Examples of traces of post-stimulus recordings with subthreshold (0.16, 0.4 g) and threshold (0.6 g) von Frey mechanical stimulation of the periorbital region (assessed as the minimum von Frey force required to induce an action potential when applied on the cell’s receptive field)