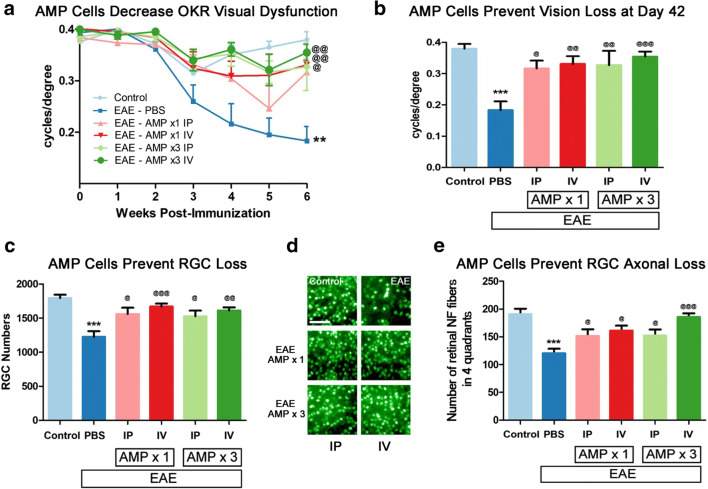
Fig. 4.
AMP cells attenuate visual dysfunction and RGC loss. a Visual function was evaluated by OKR weekly. Eyes of vehicle (PBS)-treated EAE mice (N = 8) showed a significant (**p < 0.01) progressive decrease in OKR scores over 6 weeks as compared with control (N = 6) mouse eyes. 3× dosing of AMP cells either IP (N = 6, @@p < 0.01) or IV (N = 9, @@p < 0.01), as well as 1× IV AMP cell treatment (N = 7, @p < 0.05), significantly attenuated vision loss over 6 weeks, while 1× IP (N = 6) AMP cell administration induced a non-significant trend in improved OKR responses. b Final visual function measured on day 42 p.i. showed that the significant (***p < 0.001) decrease in OKR responses in vehicle-treated EAE mice as compared with control mice was significantly prevented in all AMP cell treatment groups (@p < 0.05; @@p < 0.01); @@@p < 0.001). c To evaluate RGC loss, retinas were isolated at day 42 p.i., stained with Brn3a antibodies, and counted by a masked investigator. The significant (***p < 0.001) RGC loss found in vehicle-treated EAE mice as compared with control mice was significantly prevented in all AMP cell treatment groups (@p < 0.05; @@p < 0.01); @@@p < 0.001). d Representative images showing RGCs in one field from one retina from each treatment group (original magnification × 20, Scale bars: 50 μM) demonstrate the reduced RGC numbers induced by EAE and prevented by AMP cell treatment. e To evaluate axonal loss in the retina, retinas were isolated at day 42 p.i., stained with Neurofilament RT-97 antibodies and axonal fibers were counted by a masked investigator. Significant (***p < 0.001) axonal loss found in vehicle-treated EAE mice as compared with control mice was significantly prevented in all AMP cell treatment groups (@p < 0.05; @@@p < 0.001). Data represent mean ± SEM of measurements from the right eye of each mouse