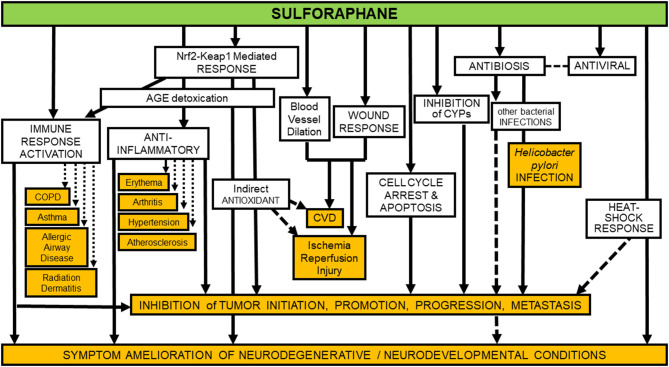
Figure 3.
Identified preventive and protective molecular mechanisms of sulforaphane are manifold. Unfilled boxes show some of the more robustly documented mechanisms, whereas orange-filled boxes indicate some of the more well-documented diseases, syndromes, and conditions against which sulforaphane's efficacy has been assessed in clinical, animal, and in-vitro studies. Mechanisms involved in inhibition of tumor initiation, promotion, progression and metastasis (second box from bottom of figure) are too numerous to fully itemize on a simplistic diagram such as this, but in addition to those indicated by arrows directed toward the box, they include: inhibition of NFκB, HDACs, Pgp, MRP-1, BCRP, STAT3, MEKK1 activity, AP-1 DNA binding, and tubulin polymerization; degradation of α and β-tubulin; down-regulation of cyclin B1, cdk1, cdc25B, cdc25C, HIF, VEGF, VEGF receptor, MMP-2, and MMP-9; modulation of Bcl-2 family proteins; and activation of caspases (87).