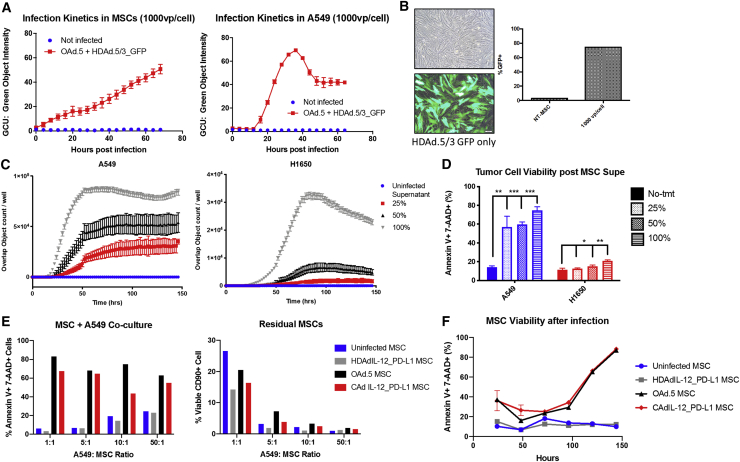
Figure 1.
MSCs are susceptible to combinatorial Ad vector (CAd) infection and produce functional cytotoxic virus
(A) MSCs (left) and A549 lung tumor cells (right) were infected with 100 vp OAd.5 and 1,000 vp HDAd.5/3-expressing GFP. GFP expression was detected by Incucyte live image analysis over time indicated by GCU, green object intensity. (B) MSCs were imaged 72 h post infection with 1,000 vp HDAd.5/3-expressing GFP. Cells were collected and percent GFP was measured by flow cytometry. (C) MSCs were infected with 100 vp OAd.5-expressing RFP and 1,000 vp HDAd.5/3-expressing GFP. Supernatant was collected 72 h post infection and applied to A549 and H1650 cells at 100%, 50%, and 25% dilutions. The number of cells expressing both RFP and GFP were measured by Incucyte indicated by Overlap Object count/well. (D) Viability was measured at 6 days post supernatant addition through 7-AAD and Annexin V staining analyzed by flow cytometry. Significance was determined by Student’s t test for each dilution compared to the no-treatment (No-tmt) group. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Error bars represent standard deviation. (E) Infected MSCs co-cultured with different ratios of tumor cells 24 h post MSC infection. Tumor cell viability was determined by gating on CD90-A549 cells and measured 7-AAD and Annexin V staining (left). The percentage of MSCs remaining in co-culture after 5 days is shown to the right as determined by CD90 positivity through fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis. (F) Viability of MSCs post infection in vitro over time. MSC cell death determined by Annexin V+ 7-AAD+ staining and analyzed by flow cytometry. n = 2 MSC donors.