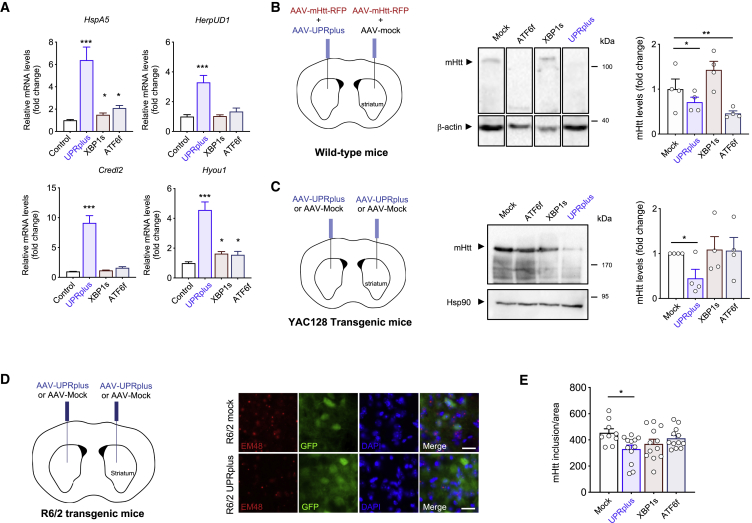
Figure 5.
UPRplus expression decreases mutant huntingtin aggregation in vivo
(A) Primary cortical neurons were infected at 1 day in vitro (DIV) with adeno-associated virus (AAV) encoding for UPRplus, ATF6f, XBP1s, or empty vector (control). After 6 DIV, expression levels of UPR-target genes were measured by real-time RT-PCR. All samples were normalized to β-actin levels. mRNA levels are expressed as fold increase over the value obtained in control cells infected with AAV-empty (control). (B) Three-month-old WT mice were co-injected into the striatum by stereotaxis with a mixture of AAVs encoding a mHtt construct (Htt588Q95-mRFP) together with AAV-UPRplus, AAV-XBP1s, AAV-ATF6f, or AAV-mock (control). Schematic representation of the experimental strategy is shown (left panel). Animals were then euthanized at 2 weeks post-injection and brain striatum tissue was dissected for western blot analysis using an anti-polyQ antibody. β-Actin levels were analyzed as a loading control (middle panel). HMW mHtt aggregates were quantified and normalized to β-actin levels (right panel) (AAV-mock, n = 4; AAV-UPRplus, n = 4; AAV-XBP1s, n = 4; AAV-ATF6f, n = 4). (C) Three-month-old YAC128 mice were injected into the striatum with AAV-UPRplus, AAV-ATF6f, AAV-XBP1s, or AAV-mock vector (control) using bilateral stereotaxis surgery. Schematic representation of the experimental strategy is shown (left panel). Four weeks later the striatum region was dissected and mHtt aggregation levels were analyzed by western blot using an anti-polyQ antibody (middle panel). mHtt aggregate levels were quantified and normalized to Hsp90 levels (right panel). In (B) and (C), the mean and standard error are presented for the analysis of four animals per group. (D) R6/2 mice were injected at 4 weeks of age with a mixture of AAV-EGFP and AAV-XBP1s (n = 4), AAV-ATF6f (n = 4), AAV-UPRplus (n = 4), or AAV-mock (control) (n = 3) into the striatum using bilateral stereotaxis (left panel). Four weeks after injection, the brain was extracted and coronal slices from the striatum were obtained. mHtt was detected using the anti-huntingtin EM48 antibody (red) by fluorescence microscopy (red). EGFP expression was monitored as control for the injection (green). Nuclei were stained using DAPI (blue) (scale bars, 20 μm) (right panel). (E) High-resolution images of the slices were obtained and quantification of mHtt was performed using ImageJ software. The quantification of the number of mHtt inclusions was performed by total area. Statistical analysis was performed using Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.