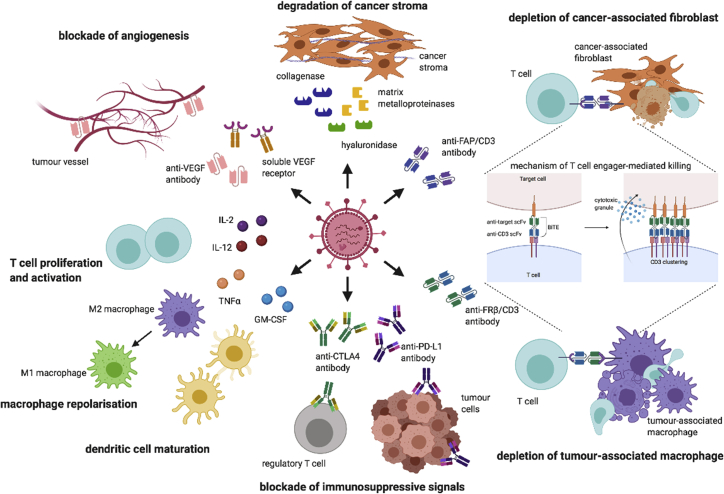
Figure 1.
Strategies of armed OVs for targeting the TME
OVs infect and lyse cancer cells, releasing the armed biologics to the TME. Matrix-degrading enzymes such as hyaluronidase, collagenase, and matrix metalloproteinase are used to degrade the dense and viscous cancer stroma. Bispecific antibodies such as bispecific T cell engager targeting FAP and FRβ are designed to selective deplete cancer-associated fibroblasts and immunosuppressive M2 macrophages, and activate endogenous T cells independent of the MHC class I molecule. Monovalent antibodies such as anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-L1 antibodies can also be encoded by OVs to block the inhibitory receptors on regulatory T cells and tumor cells. In addition, cytokines such as GM-CSF and TNF-α can be armed in OVs to promote dendritic cell maturation and macrophage repolarization. IL-2 and IL-12 have also been used to promote T cell proliferation and activation. Soluble VEGFR receptor composed of VEGFR fused to an Fc domain is encoded by OVs to block the VEGF/VEGFR pathway for suppressing angiogenesis. CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4; FAP, fibroblast activation protein α; FRβ, folate receptor β; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL-2, interleukin-2; IL-12, interleukin-12; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, VEGF receptor.