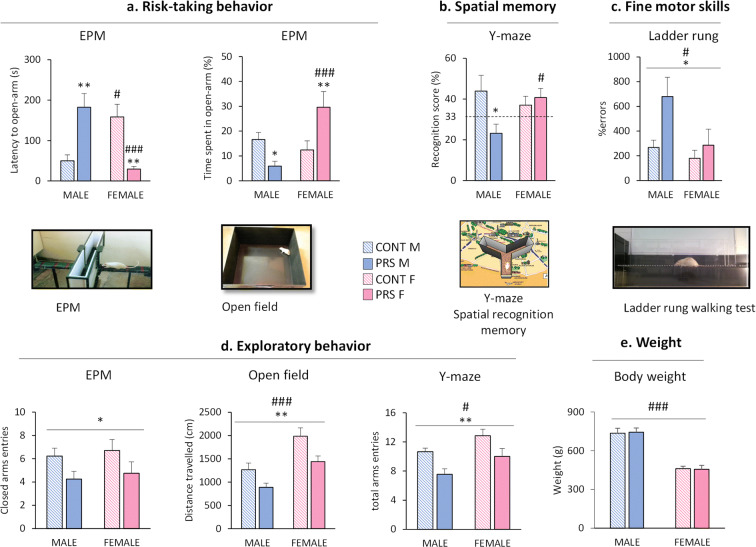
Fig. 2.
Sex-specific effects of PRS on behavior of aged rats. Risk-taking behavior in the EPM is shown in a. The latency to the open arm and time spent in the open arm were the two parameters analyzed. The spatial recognition memory was studied using the Y-maze. The recognition score (%) is represented in b. The ladder rung-walking test was used to study the fine motor skills. The percentage of errors is shown in c. Exploratory behavior was analyzed in the EPM test considering the closed arm entries, the open-field with the distance traveled, and the Y-maze test, where we analyzed the total arm entries (d). The weight of the animals before behavioral assessment (21 months old) is represented in e. Error bars represent the SEM. CONT vs PRS * = p < 0.05; ** = p < 0.01. Males vs females # = p < 0.05; ## = p < 0.01; ### = p < 0.001