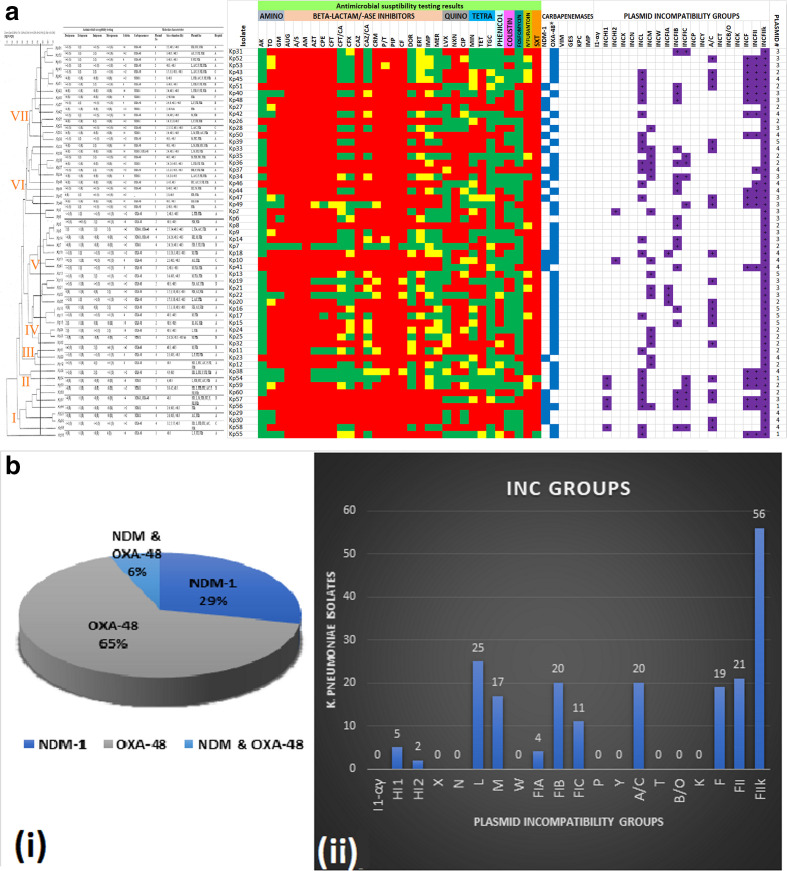
Fig. 1.
Antibiotic susceptibility patterns, carbapenemase genes and plasmid characteristics of 56 clinical K. pneumoniae isolates arranged according to their clustering patterns on a REP-PCR dendrogram. The isolates clustered into seven main clusters/clades, based on their gel patterns. Antibiotic resistance is shown as red, intermediate resistance is shown as yellow and susceptibility is shown as green. Carbapenemase genes are shown as blue and plasmid replicons are shown as violet/mauve. The number of plasmids is shown in the last column (a). Most of the isolates harboured OXA-48 (65 %) compared to NDM-1 (29 %) whilst a minority had both genes (6 %) (i). IncF plasmid replicons were the commonest plasmid types, being found in all the isolates; IncL, A/C and IncM were also common types (ii) (b).