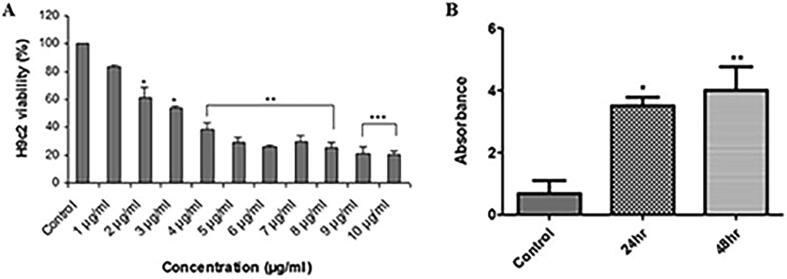
Fig. 2.
AgNPs exposure affects percent viability and DNA fragmentation in H9c2 cardiac cells. (A) Cells were treated with different AgNPs concentrations from 0 to 10 µg/ml for 48 hr. Cell viability (n = 3) was evaluated by MTT reduction assay. AgNPs exposure inhibited cell viability in a dose-dependent manner. (B) BrdU analysis in control and AgNPs treated H9c2 cells following 24 hr and 48 hr time interval. Histograms show the data obtained after anti-BrdU staining. AgNPs exposure of H9c2 cells caused a significant time-dependent increase in DNA strand break signifying cell death by apoptosis. The variations in their levels were analyzed statistically. Data are presented as the mean ± SE of three independent experiments. (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).