FIGURE 1.
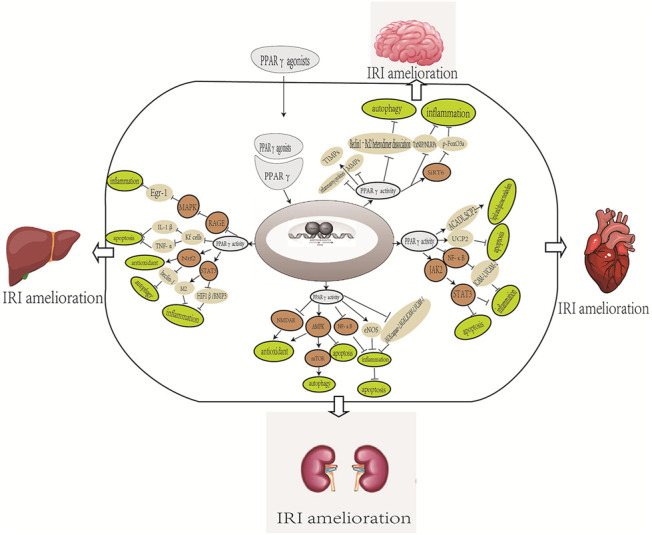
Overview of the possible mechanisms of PPARγ in the organ IRI. The mechanism includes different effects of different PPARγ agonists. NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartic acid; eNOS, endothelial NO synthase; iNOS, inducible NO synthase; Nrf2, nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation end products; SIRT6P, the endogenous retinoid X receptor and sirtuin 6; Fox03a; BBB, blood–brain barrier; MMB, matrix metalloproteinase; TIMPs, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase; TXNIP, thioredoxin interacting protein; NLRP3, nod-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3; SCP2, sterol carrier protein 2; ACADI, long-chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase; UCP2, mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2.
