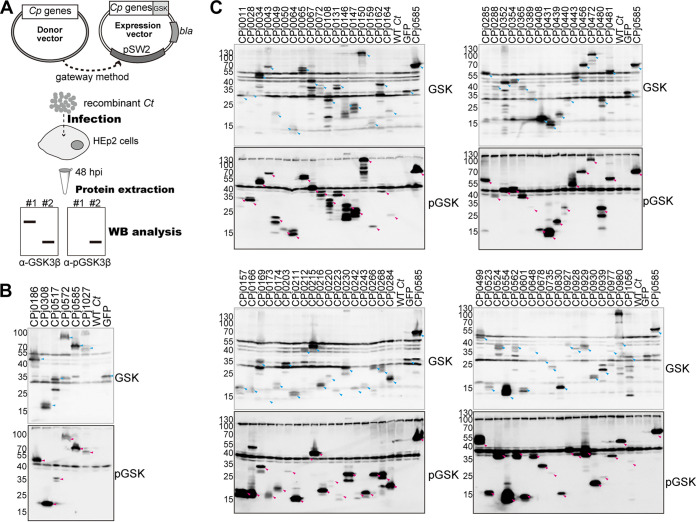
FIG 1.
Summary of C. pneumoniae ORFs identified as targets of translocation by C. trachomatis. (A) A total of 382 C. pneumoniae genes in a pDONR221 Gateway vector (entry clone) were transferred to a C. trachomatis expression plasmid (pEAS7) to generate C. pneumoniae protein fusions to a peptide tag derived from glycogen synthase kinase (GSK3β). (B, C) HEp-2 cells were infected for 48 h with C. trachomatis expressing C. pneumoniae proteins, and total proteins were extracted and analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-GSK3β antibodies to identify recombinant C. pneumoniae proteins and anti-phospho-GSK3β antibodies to identify proteins that were exposed to host cytoplasmic GSKs. Six previously characterized C. pneumoniae effectors and GFP-expressing recombinant C. trachomatis were analyzed by immunoblotting (B), and 69 novel C. pneumoniae proteins were detected by both anti-GSK3β and anti-phospho-GSK3β antibodies (C). GFP-GSK was included as a control for a nonsecreted protein. Cyan and magenta arrowheads indicate each protein detected by anti-GSK3β and anti-phospho-GSK3β antibodies, respectively.