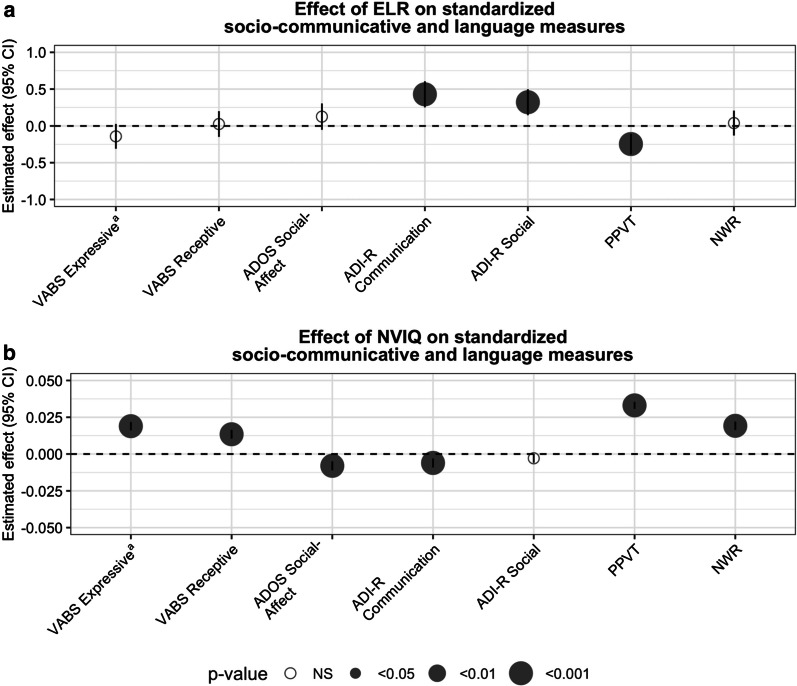
Fig. 4.
Effects of ELR and non-verbal intelligence quotient on socio-communicative and language measures in fluent speakers. Outcome measures were standardized within the sample to show effect sizes side by side. a Effect of early language regression (ELR). ELR did not have a significant effect on the expressive and receptive communicative levels measured by the Vineland (VABS) nor when socio-communicative competence was directly assessed by clinicians (ADOS social affect). Historical measures of impaired communication and social ability, retrospectively reported by parents, are associated with ELR. Lexical knowledge, measured by the PPVT, is negatively affected by ELR. The non-word repetition task score (NWR) is not significantly associated with ELR. Analyses were adjusted for NVIQ, sex, and age of assessment for historical measures. b Effect of non-verbal intelligence quotient (NVIQ). NVIQ was positively associated with levels of expressive and receptive language measured by the VABS. Higher NVIQ is protective against the severity of socio-communicative deficit measured by the ADOS. Historical measures of communication are negatively associated with NVIQ, but not social ability when measured retrospectively by the ADIR-R. Lexical knowledge and NWR are both positively associated with NVIQ. Analyses were adjusted for ELR, sex, and age of assessment for historical measures a Effect on the standardized log transformed outcome score