Fig. 5.
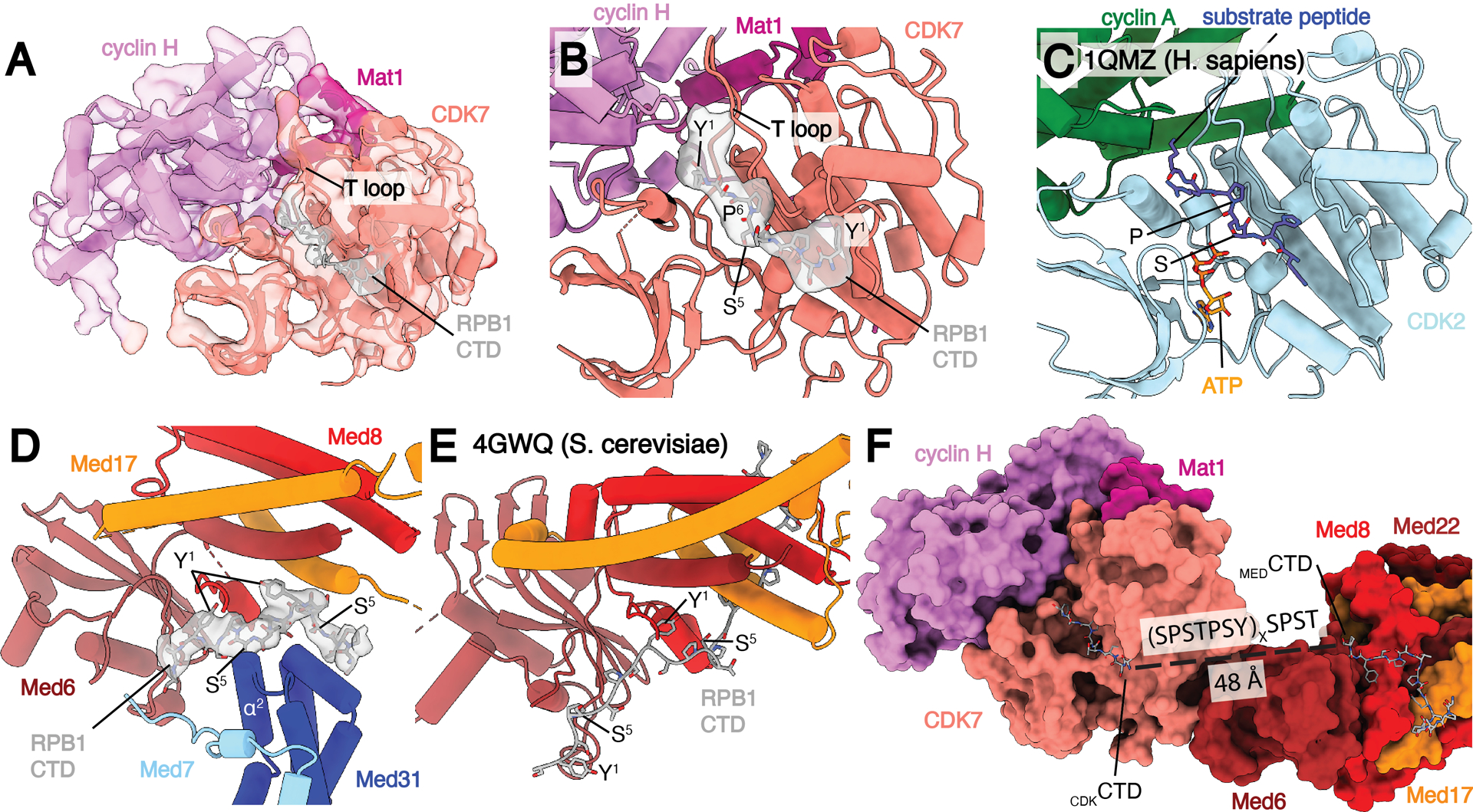
Location of RPB1 CTD binding in Med-PIC. A) Structure of the TFIIH CAK module. Segmented map of MedMiddle-CAK shows clear density representing an active conformation of the T-loop of CDK7 and density for Pol II CTD in the active site of CDK7. B) Model of the CAK module with density observed for the CDKCTD in the active site. A consensus sequence of the Pol II CTD is modeled due to limited resolution. The T-loop is in the extended, active conformation. C) Model of the CDK2-cyclin A-substrate peptide structure shows high similarity to the CAK module structure with the conserved SP motif that is common to substrates of both enzymes. D) Model and density of MEDCTD with interacting subunits of MedHead and MedMiddle. S5 makes close contacts with α2 of Med31, preventing binding of phosphorylated repeats in this location. E) Model of MEDCTD in the yeast MedHead crystal structure shows a more extensive interface between MEDCTD and MedHead than in the Med-PIC, likely due to the presence of MedMiddle in the Med-PIC. F) View of CDKCTD and MEDCTD within the human Med-PIC structure. Based on the directionality of the CTD, CDKCTD is C-terminal to MEDCTD, and the gap between them would require at least two repeats of the CTD. MedMiddle is hidden for easier visibility. Models are colored as in Figure 1. Annotated domains of Mediator are labeled in black.
