Figure 7.
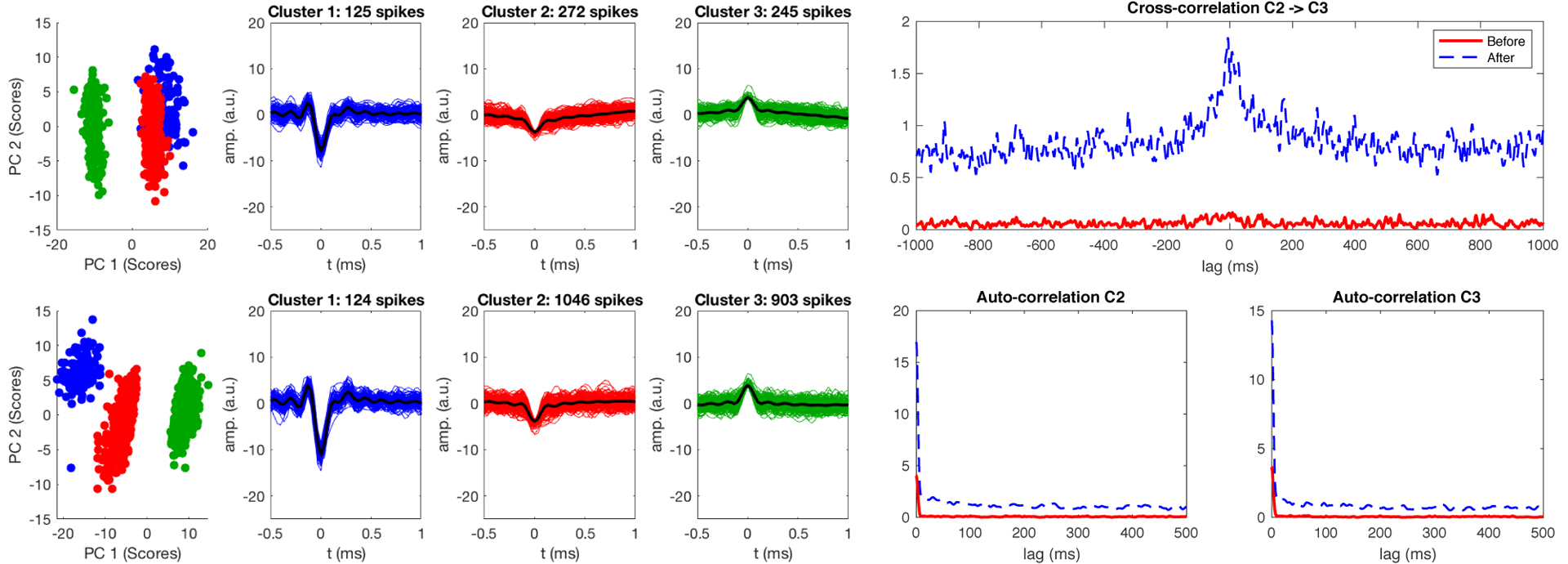
Clustering of lower SNR data before (top row) and after (bottom row) adaptive virtual referencing. The adaptive virtual reference reduces noise in spike waveforms (resulting in increased peak height due to noise level normalization), and a higher number of small spikes from multiple units (clusters 2 and 3) are detected after adaptive virtual referencing. Clusters formed from two minutes of recording data. The autocorrelation and cross-correlation of the small clusters is influenced by adaptive virtual referencing, as many more occurrences of spikes in the small amplitude clusters become measured and the underlying dynamics are better observed. Note that clusters 2 and 3 likely still contain multiple contributing neurons, as neurons farther from the recording site will generate smaller and less-distinguishable waveforms in comparison to neurons closer to the electrode (e.g. cluster 1).
