Figure 1: Age-Associated Changes in T cell and B cells.
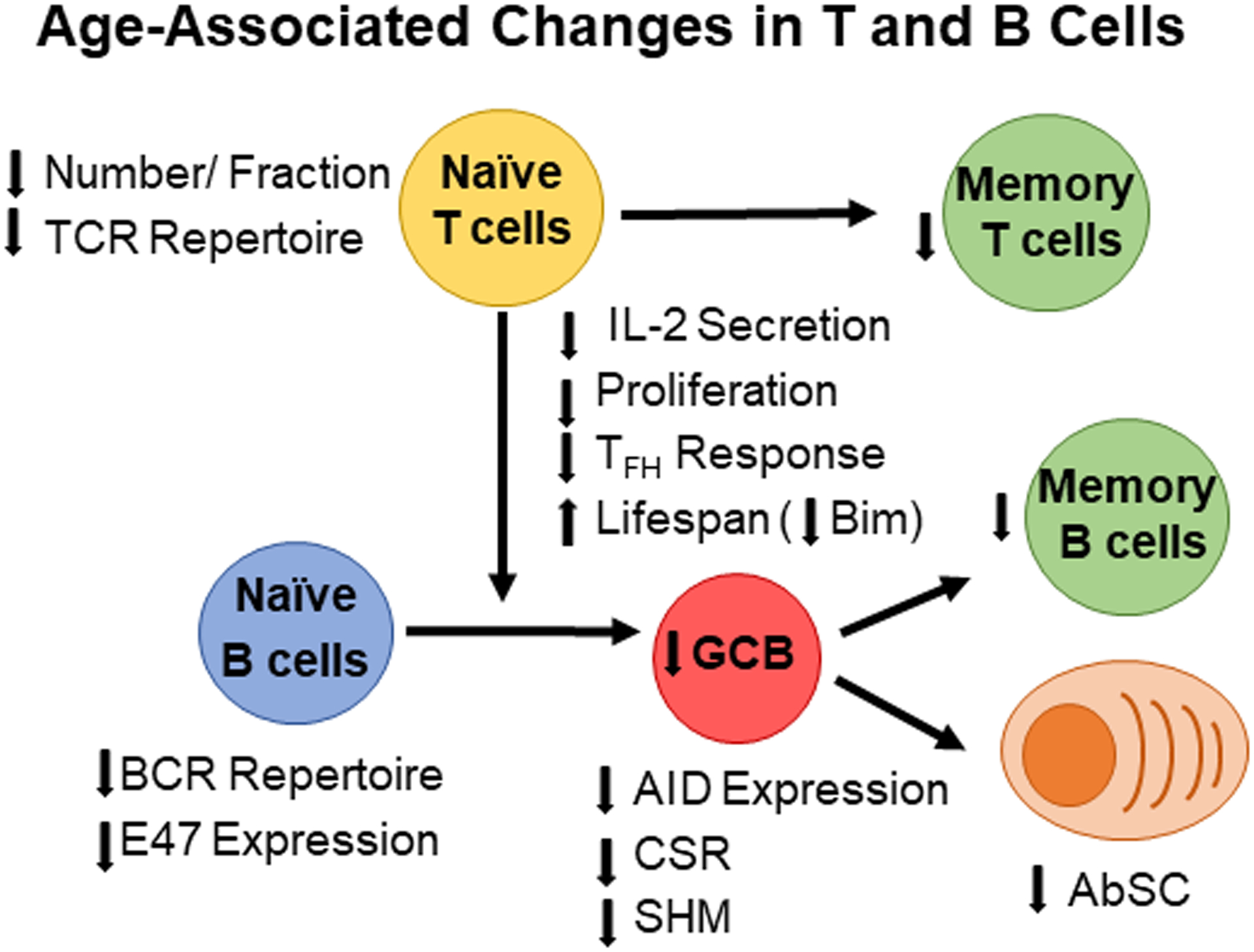
With age, the number of naïve B cells and T cells decreases leading to a smaller TCR and BCR populations and repertoires. Upon pathogen exposure, naïve CD4 T cells secrete less IL-2 leading to lower effector T cell responses including T follicular helper cells (Tfh). Lower Tfh responses decrease GCB responses, which leads to fewer memory B cells and antibody-secreting cells towards newly encountered pathogens. However, memory B cells from previous immune responses accumulate with age leading to a larger memory B cells pool in the aged.
