Figure 1. RADD detection of DNA damage within FFPE samples.
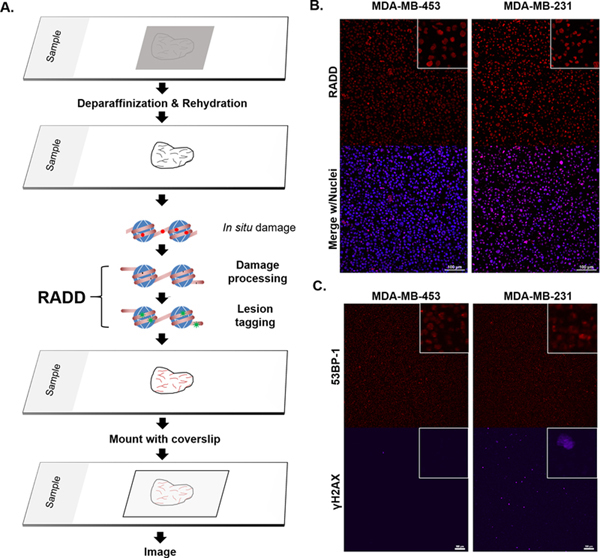
A. RADD workflow. FFPE tissue samples are deparaffinized and rehydrated. The RADD assay is performed with a cocktail of DNA repair enzymes that detects and removes damaged DNA leaving gaps where damaged bases were encountered. Lesion filling occurs with a DNA polymerase and a tagged dUTP molecule allows for fluorescent detection of the damage site. B. RADD detection of DNA lesions within FFPE immortalized cell lines. C. Strand break markers for γH2AX and 53BP-1 confirm presence of DNA damage within the FFPE samples. Scale bars 100 μm.
