Fig. (2). Effect of diet on the release of cholecystokinin (CCK) for the regulation of hepatobiliary and pancreatic functions and gastrointestinal tract motility.
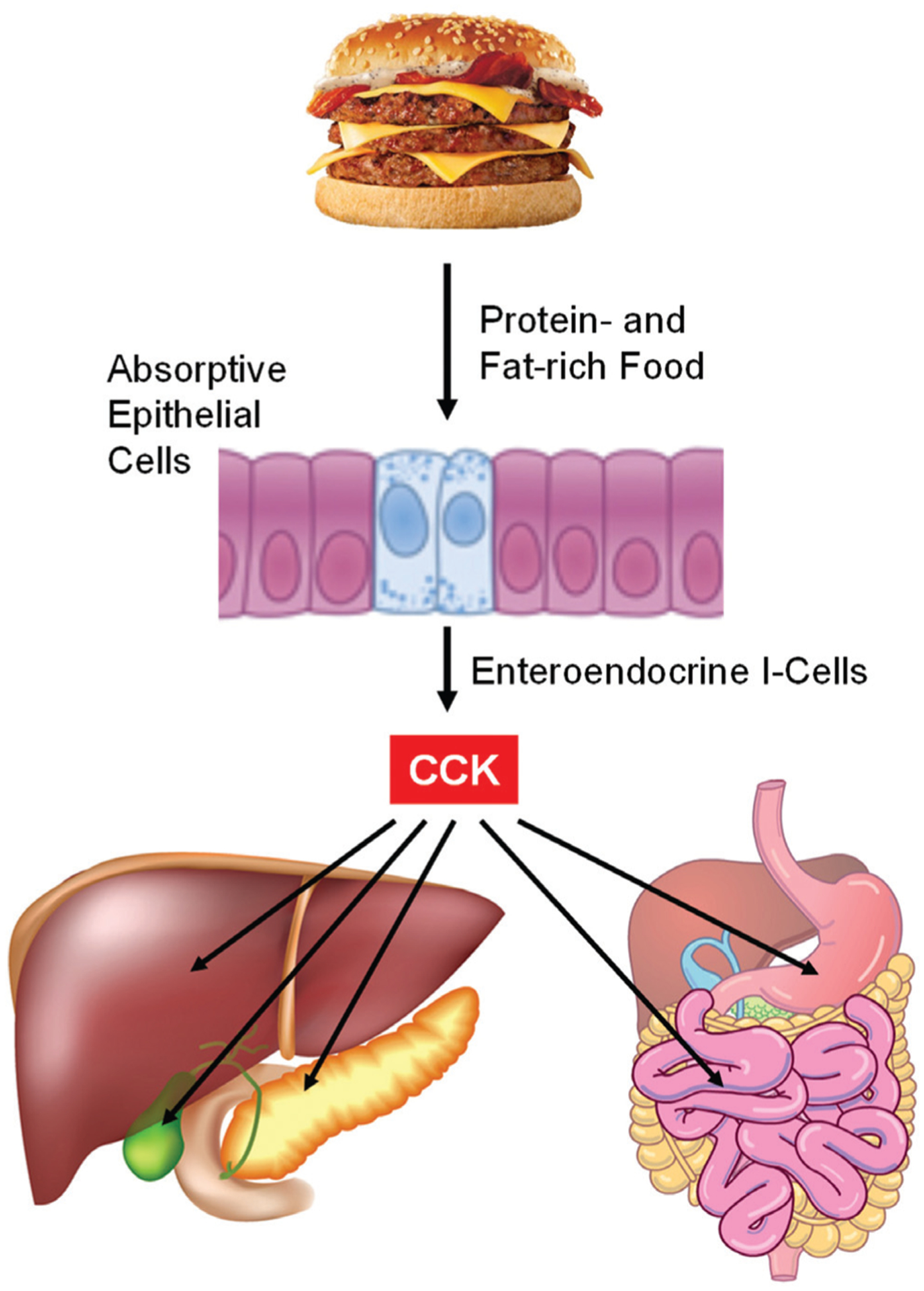
Among the nutritional components, protein- and fat-enriched food is the most important trigger stimulating CCK secretion from the intestinal endocrine I-cells. Carbohydrates stimulate only small amounts of CCK release. CCK causes gallbladder contraction by acting on gallbladder smooth muscles. CCK mainly stimulates hepatic secretion of bicarbonate from hepatic ductular cells. CCK promotes the secretion of pancreatic enzymes such as pancreatic amylase, chymotrypsinogen, and trypsinogen, as well as several small intestinal enzymes such as alkaline phosphatase, disaccharidase and enterokinase. CCK accelerates small intestinal transit through the CCK-1 receptor (CCK-1R) signaling cascade. In contrast, CCK inhibits gastric emptying. See text for more details.
