Fig. 8.3.
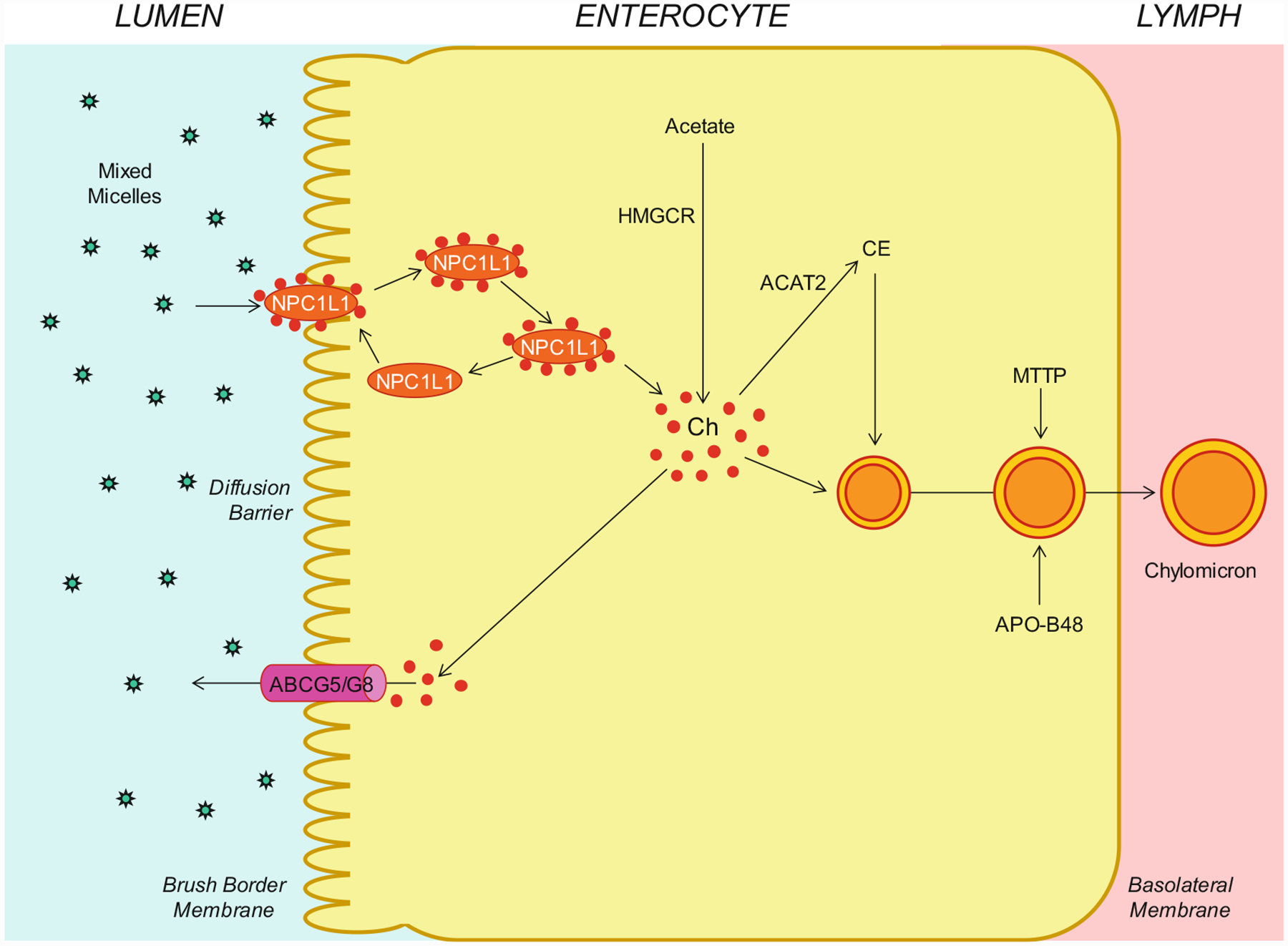
Molecular and cellular mechanisms of intestinal cholesterol absorption. Within the intestinal lumen, the micellar solubilization of sterols facilitates movement through the diffusion barrier overlying the surface of the absorptive cells in the small intestine. In the presence of bile salts, mixed micelles deliver large amounts of the cholesterol (Ch) molecules to the aqueous-membrane interface so that the uptake rate is greatly increased. The Niemann-Pick C1 like 1 (NPC1L1) protein, a sterol influx transporter, is located at the apical membrane of the enterocyte and can actively facilitate the uptake of cholesterol by promoting the passage of cholesterol across the brush border membrane of the enterocyte. NPC1L1 appears to mediate cholesterol uptake via vesicular endocytosis, and ezetimibe may inhibit cholesterol absorption by suppressing the internalization of NPC1L1/cholesterol complex. In contrast, ABCG5/G8 promote active efflux of cholesterol from the enterocyte back into the intestinal lumen for fecal excretion. The combined regulatory effects of NPC1L1 and ABCG5/G8 play a critical role in modulating the amount of cholesterol that reaches the lymph from the intestinal lumen. The absorbed cholesterol molecules, as well as some that are newly synthesized from acetate by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGCR) within the enterocytes, are esterified to fatty acids by acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase isoform 2 (ACAT2) to form cholesteryl esters (CE). All of these lipids are involved in the assembly of chylomicrons, which also requires the synthesis of apolipoprotein B-48 (apoB-48) and the activity of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTTP). The core of chylomicrons secreted in lymph contains triglycerides and cholesteryl esters, and their surface is a monolayer containing phospholipids (mainly phosphatidylcholine), unesterified cholesterol, and apolipoproteins such as apoB-48, apoA-I, and apoA-IV
