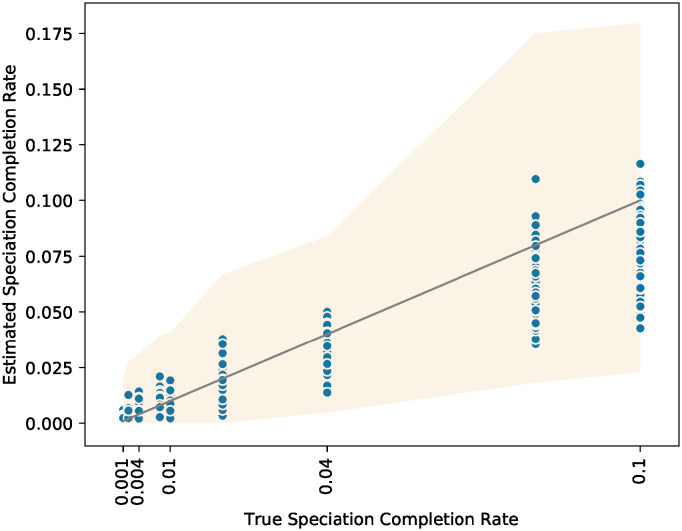
Fig 3. Accuracy of species delimitation under different levels of species constraints and dataset sizes (i.e., number of lineages in the tree).
Simulations span differing speciation-completion rates (indicated by color gradient with darker colors representing lower rates and lighter colors representing higher rates). Even with inferring the speciation-completion rate from the data, (a) recovery of the correct number of species is extremely reliable across a broad range of conditions, comparing the true number of species with the the inferred number of species; each dot corresponds to the analysis of one replicate dataset. However, whether the (b) identity of species is accurately inferred differs depending upon the size of the data set (i.e., number of lineages), the constraint level (i.e., the number of lineages with designations set a priori; e.g., “30/40” corresponds to a tree with 40 lineages, 30 of those with known species identities, and 10 lineages with inferred identities), and the particular speciation-completion rate the data were simulated under (note that this rate was inferred during the analyses). Shown are the proportion of 100 replicates for each set of conditions in which the partition with the highest probability corresponded to the correct assignments of all species identities.