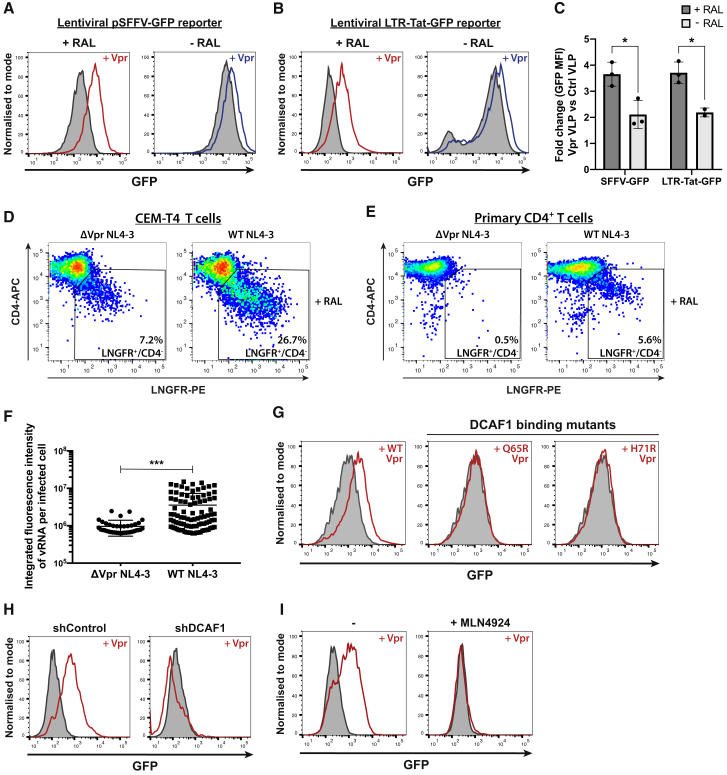
Figure 1.
HIV-1 Vpr increases gene expression from unintegrated lentiviral reporters in a cullin-RING E3 ligase dependent manner
(A–C) Unintegrated or integrated virus reporter assay. CEM-T4 T cells were co-infected with either SFFV-GFP (A) or LTR-Tat-GFP (B) lentiviral reporters and control (gray shaded) or Vpr-containing (red/blue line) VLPs ± raltegravir (RAL) treatment. GFP expression was evaluated by flow cytometry 72 h post-infection (hpi), representative example (n = 3). Quantified in (C) as the fold change in GFP mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) upon addition of Vpr versus control VLPs.
(D and E) Unintegrated ΔVpr NL4-3LNGFR has reduced gene expression. CEM-T4 T cells (D) or primary CD4+ T cells (E) were infected with WT or ΔVpr NL4-3LNGFR at equal MOI in the presence of RAL. Cells were stained with α-LNGFR and α-CD4 antibodies 48 hpi and analyzed by flow cytometry (n = 2).
(F) Unintegrated ΔVpr NL4-3GFP produces less vRNA. Jurkat T cells were infected with WT or ΔVpr NL4-3GFP in presence of RAL. 48 hpi, vRNA was detected by in situ hybridization. Scatter plot shows total vRNA fluorescence per infected cell for 500 cells/condition, filtered for cells with signal intensity ≥2xSD above background. Representative example (n = 2).
(G–I) Inhibition of CRL4DCAF1 activity abrogates Vpr phenotype. Unintegrated virus reporter assay with SFFV-GFP lentiviral reporters and control or Vpr VLPs upon: Vpr Q65R or H71R point mutation (G), shRNA knockdown of DCAF1 (H), or MLN4924 chemical cullin inhibition (I). Representative histograms (n = 2). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Error bars show standard deviation.
See also Figure S1.