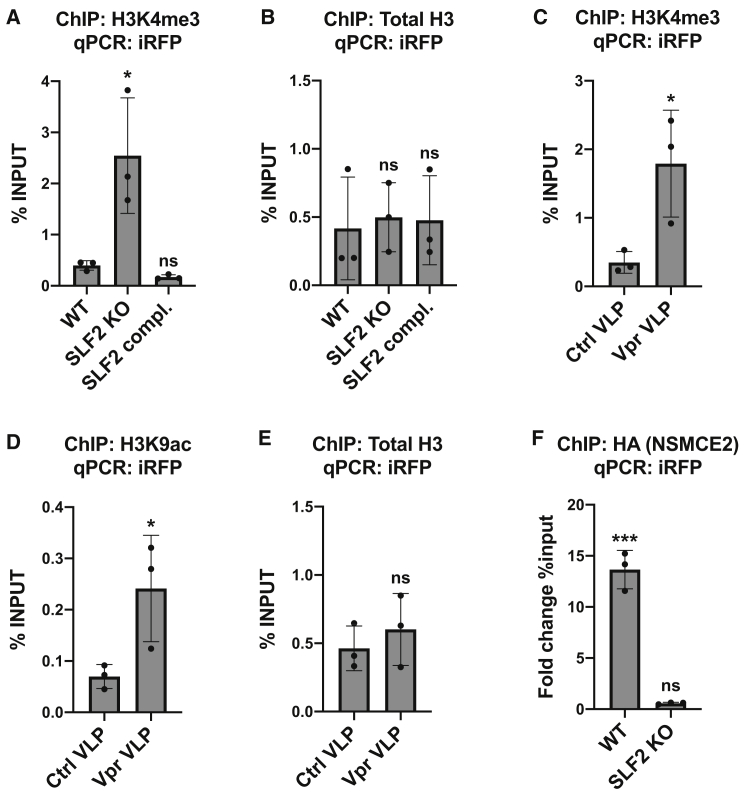
Figure 5.
The SMC5/6 complex is recruited in an SLF2-dependent manner to unintegrated lentiviral genomes leading to a loss of H3K4me3 and H3K9ac on viral chromatin
(A and B) Knockout of SLF2 increases H3K4me3 on unintegrated virus. WT, clonal SLF2 KO and SLF2 complemented SLF2 KO cells were infected with SFFV-iRFP lentiviral reporters in presence of RAL. 48 hpi, ChIP was performed using antibodies against (A) H3K4me3 and (B) total H3. qPCR data from each ChIP experiment were calculated as the percentage of input DNA. Histograms summarize data from n = 3 experiments.
(C–E) Vpr-mediated depletion of SLF2 increases H3K4me3 and H3K9ac on unintegrated virus. WT cells were co-transduced with iRFP reporters and either control or Vpr VLPs in presence of RAL. 48 hpi, ChIP was performed using antibodies against (C) H3K4me3, (D) H3K9ac, and (E) total H3, calculated as the percentage of input DNA (n = 3).
(F) The SMC5/6 complex binds unintegrated viral genomes via SLF2. WT or SLF2 KO cells expressing 3xHA-NSMCE2 were infected with SFFV-iRFP in presence of RAL. 48 hpi, ChIP was performed using antibodies against the HA-tag. Data were calculated as the fold change in percentage of input DNA compared with a matched control ChIP experiment performed in reporter-infected WT or SLF2 cells that did not express HA-NSMCE2 (n = 3). Error bars show standard deviation. ns, p > 0.05; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
See also Figure S6.