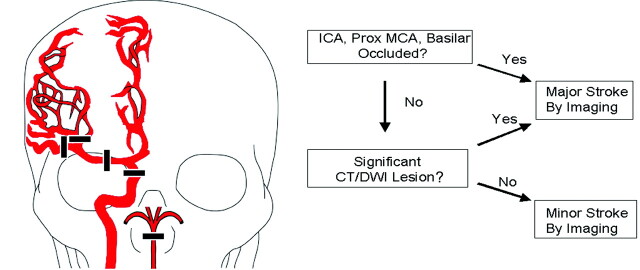
Fig 1.
Classification algorithm. Proximal cerebral artery occlusions are depicted in the drawing on the left and are defined as including the following arteries: distal (intracranial) ICA, proximal (M1 or M2) MCA, and/or basilar artery (BA). As shown in the algorithm on the right, the first step was evaluation of CTA or MRA data to identify apparent proximal cerebral artery occlusions. If no proximal cerebral artery occlusion was found, the noncontrast CT or diffusion MR imaging data were reviewed for evidence of a large acute ischemic infarct as defined in the “Materials and Methods” section. If a large CT or DWI abnormality was detected, the patient was classified as having a major stroke. All other circumstances resulted in classification as a minor stroke by imaging.