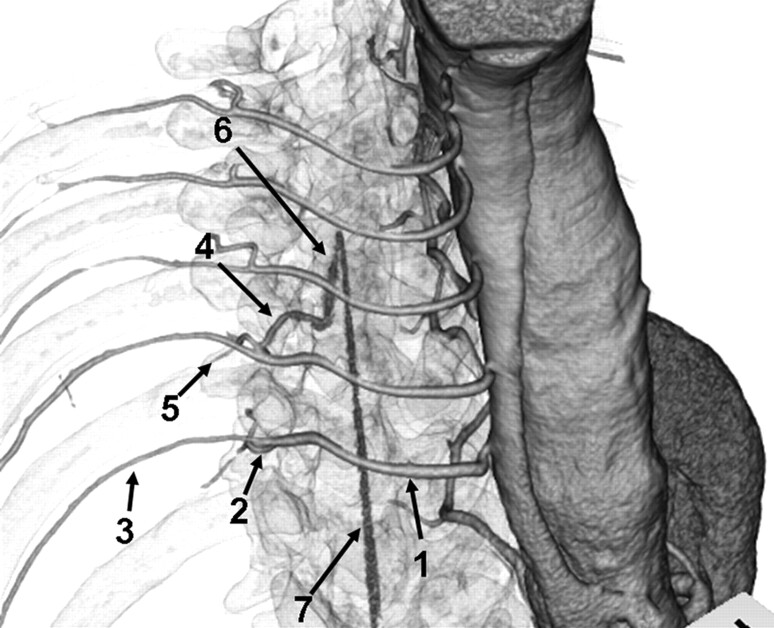
Fig 1.
Anatomic course of the AKA. Right anterosuperior view of a 3D volume-rendered CT image of IACTA with semitransparent skeletal system. Intercostal and lumbar arteries (1) originate from the aorta, and divide into posterior (2) and anterior (3) branches. Anterior branches run through the intercostal groove. Posterior branches subdivide into the radiculomedullary artery (4) and muscular branch (5). Radiculomedullary artery courses to the spine and enters the vertebral foramen. The AKA (6) is the largest anterior radiculomedullary artery and joins the anterior spinal artery (7) in a characteristic hairpin curve.