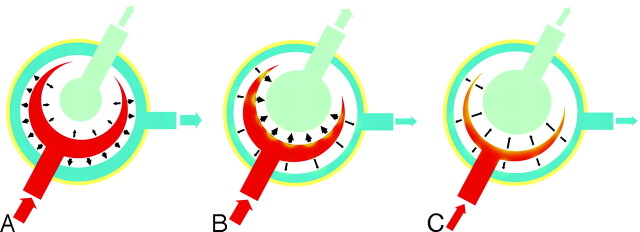
Fig 5.
Proposed model demonstrating SV changes in NPH. A, In healthy subjects, expansion of the cerebral hemispheres occurs both outward and inward. The outward expansion produces venous blood outflow as a result of compression on the cortical veins. Inward expansion produces flow of CSF into the aqueduct as a result of compression of the lateral and third ventricles. B, In communicating hydrocephalus, the brain has already expanded outward during diastole, compressing the cortical veins. However, during systole, with arterial blood entering, the systolic expansion is directed inwards, resulting in a much greater SV in the aqueduct. C, Progressive ischemia and a reduction of arterial inflow results in a decreased “ventricular CSF pump.”