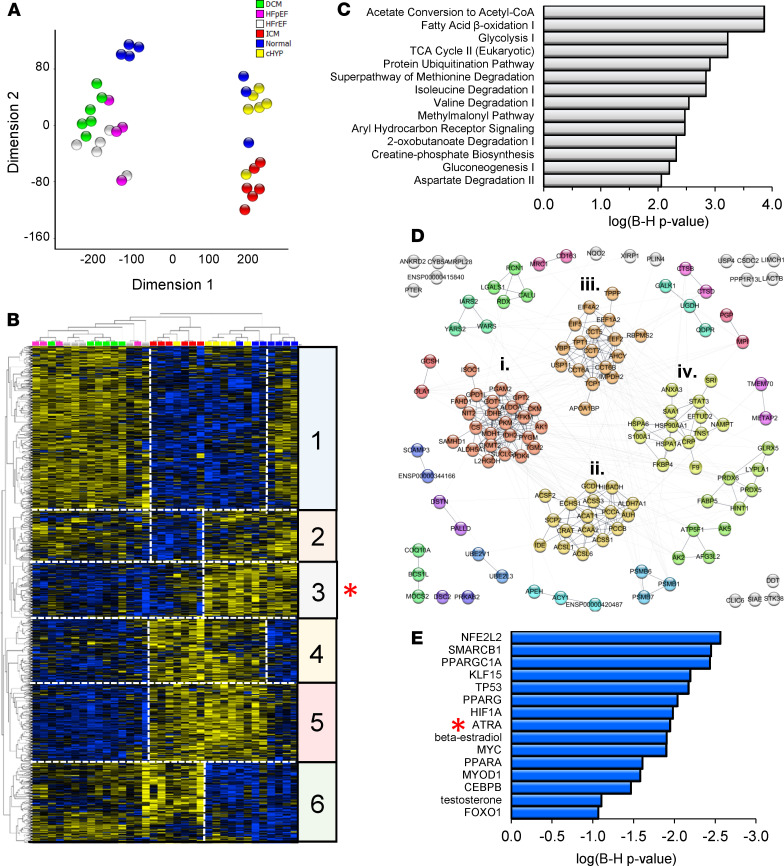
Figure 1. Human cardiac proteomes are consistent with a decline of the vitamin A metabolite and transcriptionally active hormone, ATRA, across human heart failure etiologies.
(A) Dimension reduction (t-SNE) of significantly regulated proteins across 4 HF etiologies and compensated hypertrophy (LIMMA, P < 0.05). Normal, myocardium from healthy donors (blue; n = 7); cHYP, compensated hypertrophy (yellow; n = 6); HFrEF, HF with reduced ejection fraction (white; n = 5); HFpEF, HF with preserved ejection fraction (pink; n = 4); IDCM, idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (green; n = 6); ICM, ischemic cardiomyopathy (red; n = 6). HFrEF, HFpEF, and IDCM proteomes share substantial similarity, whereas ICM has a distinctive biosignature. (B) Hierarchical clustering of significantly regulated proteins (blue, downregulated; yellow, upregulated). HF samples follow the color scheme from A. Protein levels largely correlate across HFpEF, HFrEF, and IDCM (e.g., clusters 1, 4, and 5). Cluster 2 depicts proteins uniquely downregulated in ICM. Clusters 3 and 6 represent proteins similarly regulated across HF etiologies. Specifically, cluster 3 (red asterisk) represents 132 proteins that are downregulated in most HF patients. (C) Pathway analysis showed that these proteins fall into pathways widely viewed as metabolic hallmarks of HF. (D) Coordinately downregulated proteins constitute a bona fide multimodular protein association network. (E) Upstream regulator analysis to identify transcriptional programs that might explain coordinate downregulation and activity of the network. ATRA (red asterisk) activity is inferred to decrease.