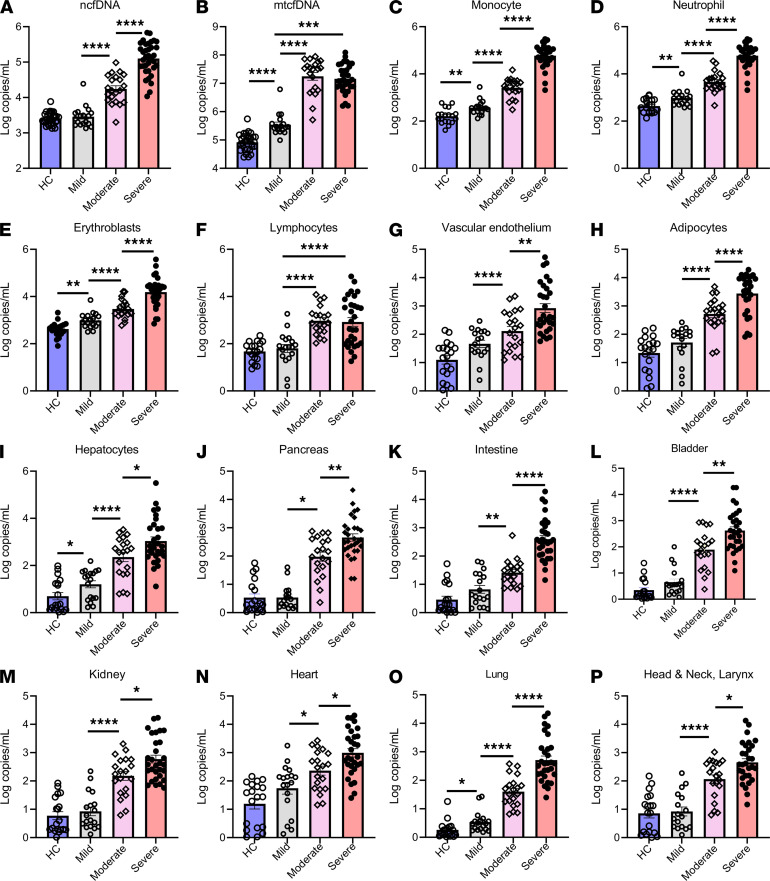
Figure 7. Plasma cfDNA levels for COVID-19 patients by severity.
(A and B) Plasma cfDNA measures compared for healthy controls (HC) shown in light blue (n = 31) and COVID-19 patients. COVID-19 patients were categorized by maximum disease severity during their illness using the WHO scale; 1–2 represents patients with mild disease not requiring hospitalization (mild) shown in gray (n = 18), 3–4 represents hospitalized patients not requiring intensive care (moderate) shown in light pink (n = 20), and 5–8 represents hospitalized patients requiring intensive care unit care (severe) shown in light red (n = 30). Only cfDNA measurements early in the COVID-19 course were considered (the first sample per patient, typically days 0–2 of admission for hospitalized patients or close to testing for patients with mild COVID-19). C–K represent cfDNA from different tissue types grouped by patient categories: (C) monocytes, (D) neutrophils, (E) erythroblasts, (F) lymphocytes, (G) vascular endothelial cells, (H) adipocytes, (I) hepatocytes, (J) pancreas, (K) bladder, (L) colon enterocytes, (M) kidney, (N) heart, (O) lung, and (P) head and neck larynx. Bar graphs expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance levels for each pairwise comparison were determined using adjusted P values computed based on Hommel’s procedure. Adjusted P values are shown. P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.