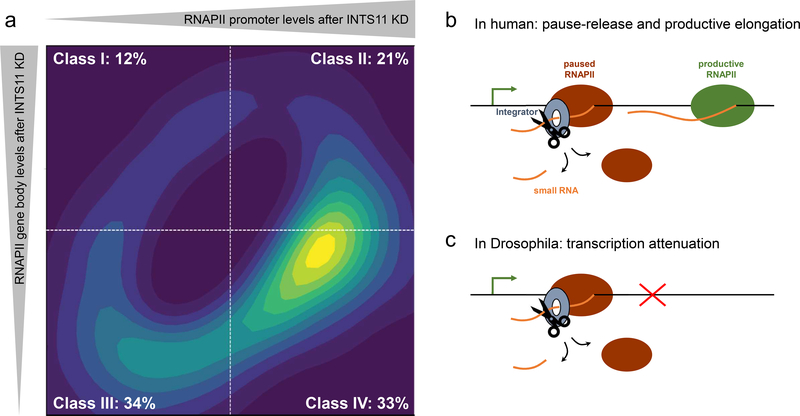
Figure 2. Integrator’s main functions on coding genes in human and Drosophila.
a) The travelling matrix separates positional RNAPII changes at promoters and gene bodies into four classes. Graphical depiction of ~3100 significant Integrator-responsive genes [19]. In human, INTS11 depletion predominantly leads to downregulation of actively engaged RNAPII (class III and IV: 67%). Class IV genes are additionally characterized by increased RNAPII pause (33%). b and c) Model representation of Integrator’s functions in human and Drosophila. b) The Integrator complex cleaves promoter-associated small transcripts to allow paused RNAPII eviction and transcriptional elongation by productive RNAPII (class IV). c) Integrator is required for the premature termination (attenuation) of RNAPII transcription.