Figure 1. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) as a tool to examine and modulate human brain circuits.
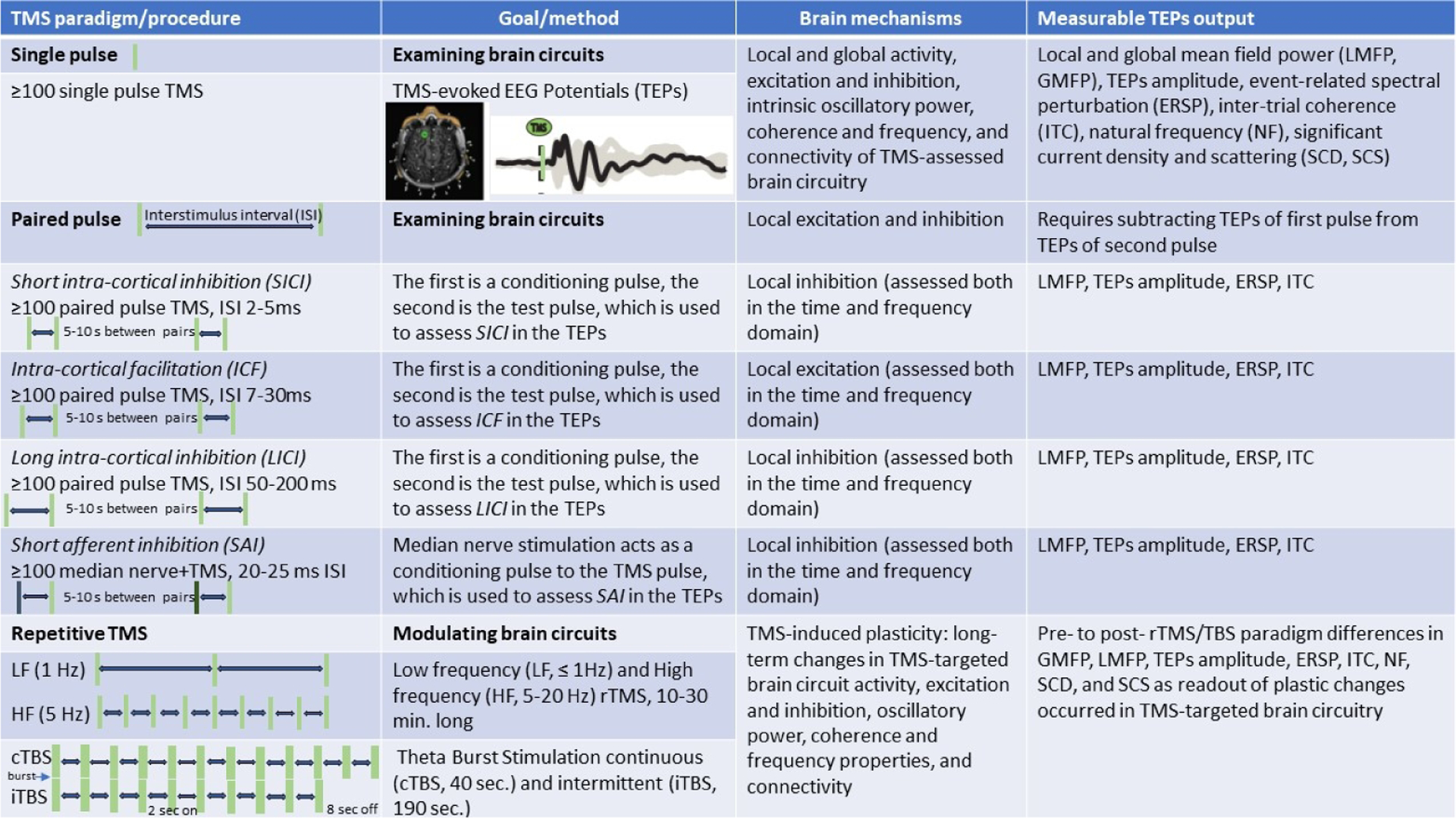
TMS paradigms (single pulse, paired pulse, repetitive TMS) and procedures (number of stimuli, interstimulus interval), goals (probing or modulating) and method (collecting TMS-evoked EEG potentials, or TEPs), brain mechanisms (local and global activity, excitation, inhibition, oscillatory activity, and connectivity), and measurable TEPs output (GMFP, LMFP, TEPs amplitude, ERSP, ITC, NF, SCD, and SCS) are presented.
