Figure 1. Inhibition and Allosteric Activation of the PRC2 Core.
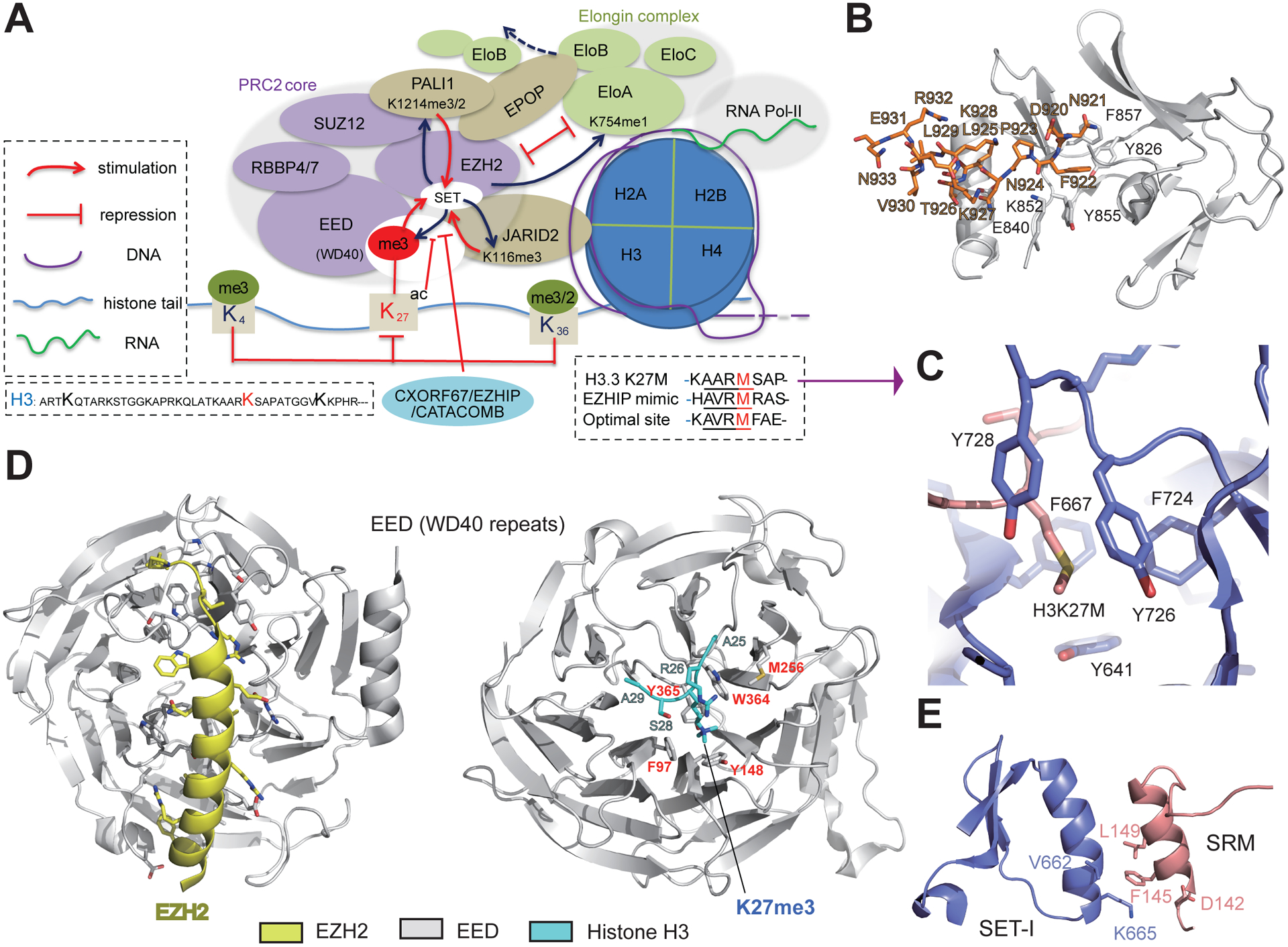
(A) Inhibition and activation of PRC2 ‘core’ activity are mediated by both ‘core’ and ‘non-core’ subunits, as well as by the chromatin environment (e.g., histone post-translational modifications and nascent RNA). EZHIP/CATACOMB mimics the K27M ‘oncohistone’ mutant of histone H3 (box on the right) and suppresses PRC2 catalytic activity via competitive inhibition. Conversely, EED binding to H3 trimethylated on Lys27 (H3K27me3) via its WD40 repeat leads to allosteric activation of PRC2:EZH2. In addition to H3K27, PRC2 also methylates the cofactors JARID2 and PALI1, and the trimethylated cofactors can mimic H3K27me3 and be read by EED for PRC2 allosteric activation. PRC2 also methylates EloA, a subunit of the Elongin complex, to inhibit Elongin-mediated transcriptional elongation. In addition, EPOP, a ‘non-core’ subunit of PRC2.1, can sequester EloB/C away from the Elongin complex, thereby downregulating target gene expression. (B) The autoinhibited conformation of the catalytic center of the fungus Chaetomium thermophilum PRC2 (PDB code 5BJS). The catalytic domain is shown as a cartoon in white, and the post-SET subdomain is shown as orange sticks. (C) Interaction between the oncohistone H3K27M and the active site of EZH2. (D) Structures showing EED in complex with the N terminus of EZH2 (left; PDB code 2QXV) and EED in complex with H3K27me3 peptide (right; PDB 3IIW). The N terminus of EZH2 is shown in yellow (left) and EED in gray, with its H3K27me3-recognizing residues labeled in red (right). (E) Binding interface between EZH2 SRM and SETI motifs (PDB 5HYN). Residues involving in interactions for allosteric activation are shown as sticks.
