Figure 2. De Novo Targeting and Spreading of PRC2 on Chromatin versus its Eviction and Functional Restriction in Mammalian Cells.
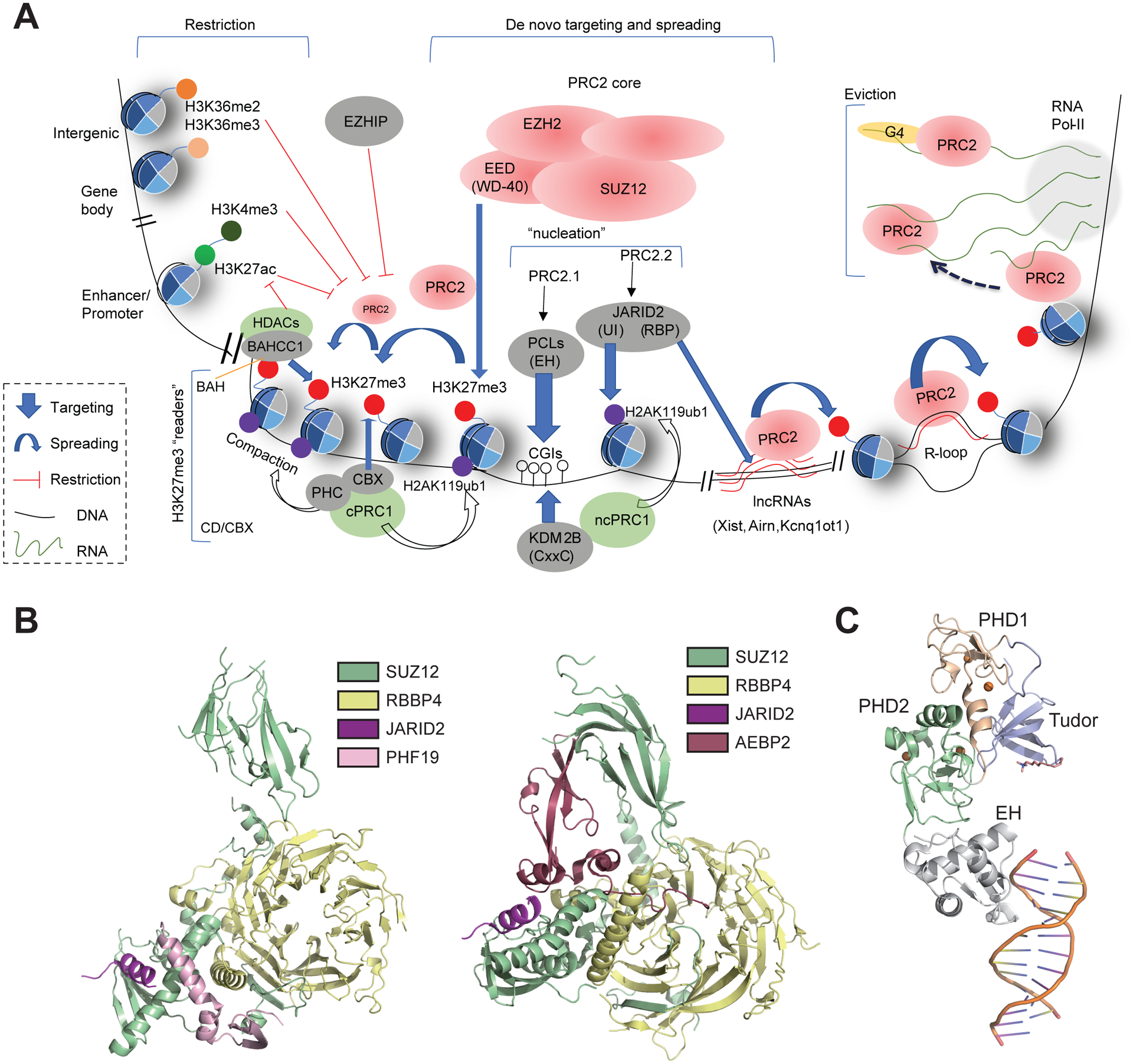
(A) (Top left) Both PRC2 enzymatic activity and Polycomb domain spreading are suppressed by gene activation-related histone post-translational modifications (PTMs), such as active promoter/enhancer-associated histone H3 Lys27 acetylation (H3K27ac)/Lys4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) and transcription-associated Lys36 trimethylation (H3K36me3; located within gene bodies); H3 Lys36 dimethylation (H3K36me2), that is deposited at intergenic regions or promoters, also inhibits PRC2-mediated H3K27me3 deposition/spreading. Likewise, EZHIP, which binds to EZH2 SET domain, impedes H3K27me3 deposition/spreading. (Middle) Reciprocal recruitment between PRC1 and PRC2 to establish Polycomb domains in the genome. On the one hand, the chromatin binding by PCLs [notably via its EH module that binds to unmethylated CpG-rich islands (CGIs) and/or G+C-rich elements] mediates de novo targeting of cPRC1, which deposits H3K27me3; this H3K27me3 can be recognized by EED, which ‘kicks off’ PRC2.1 spreading, and can in addition be ‘read’ by CBX within the canonical PRC1 complex (cPRC1) for deposition of histone H2A ubiquitinated on Lys119 (H2AK119ub1). On the other hand, a noncanonical PRC1 complex (ncPRC1) is recruited independently by a DNA-binding factor, such as KDM2B (which binds to unmethylated CGIs via its CxxC motif), and catalyzes H2AK119ub1; this H2AK119ub1 is subsequently bound by JARID2 (via its UI motif) to recruit/target PRC2.2 to chromatin. In addition, JARID2 binds to long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) via its RBP motif, and contributes to PRC2 spreading/deposition and Polycomb domain formation at silenced loci. R-loop is also relevant for PRC2 chromatin binding/recruitment. (Top right) PRC2 interactions with nascent RNAs. At active sites of transcription, PRC2 is evicted from chromatin via interactions with nascent precursor mRNAs, notably G-quadruplex (G4) RNA structures that have a higher affinity for PRC2 binding. Note that a different ‘RNA bridge’ model has also been proposed [79]. (Bottom left) At least two different classes of H3K27me3-specific readers (Figure 3), namely chromodomains (CDs) within CBXs in cPRC1 and BAH-containing proteins such as BAHCC1, induce chromatin compaction and histone decetylation that contribute to Polycomb-mediated gene silencing in mammalian cells. (B) Structures showing interactions between the N-terminal region of SUZ12 and a set of non-core subunits that are unique to PRC2.1 (PHF19/PCL3; left, PDB code 6NQ3) or PRC2.2 (JARID2 and AEBP2; right, PDB 5WAI). Subunits are colored as labeled. (C) Structure illustrating binding of the CG-rich double-stranded (ds)DNA by the conserved EH motif of PCLs (PHF1; PDB 5XFQ). Different domains are colored as labeled. The dsDNA is shown as a cartoon. Abbreviation: Pol II, polymerase II.
