Figure 3. Distinct Classes of Readers of H3K27me3 (Histone H3 Trimethylated on Lys27) Mediate Gene Silencing by Polycomb via Different Molecular Mechanisms.
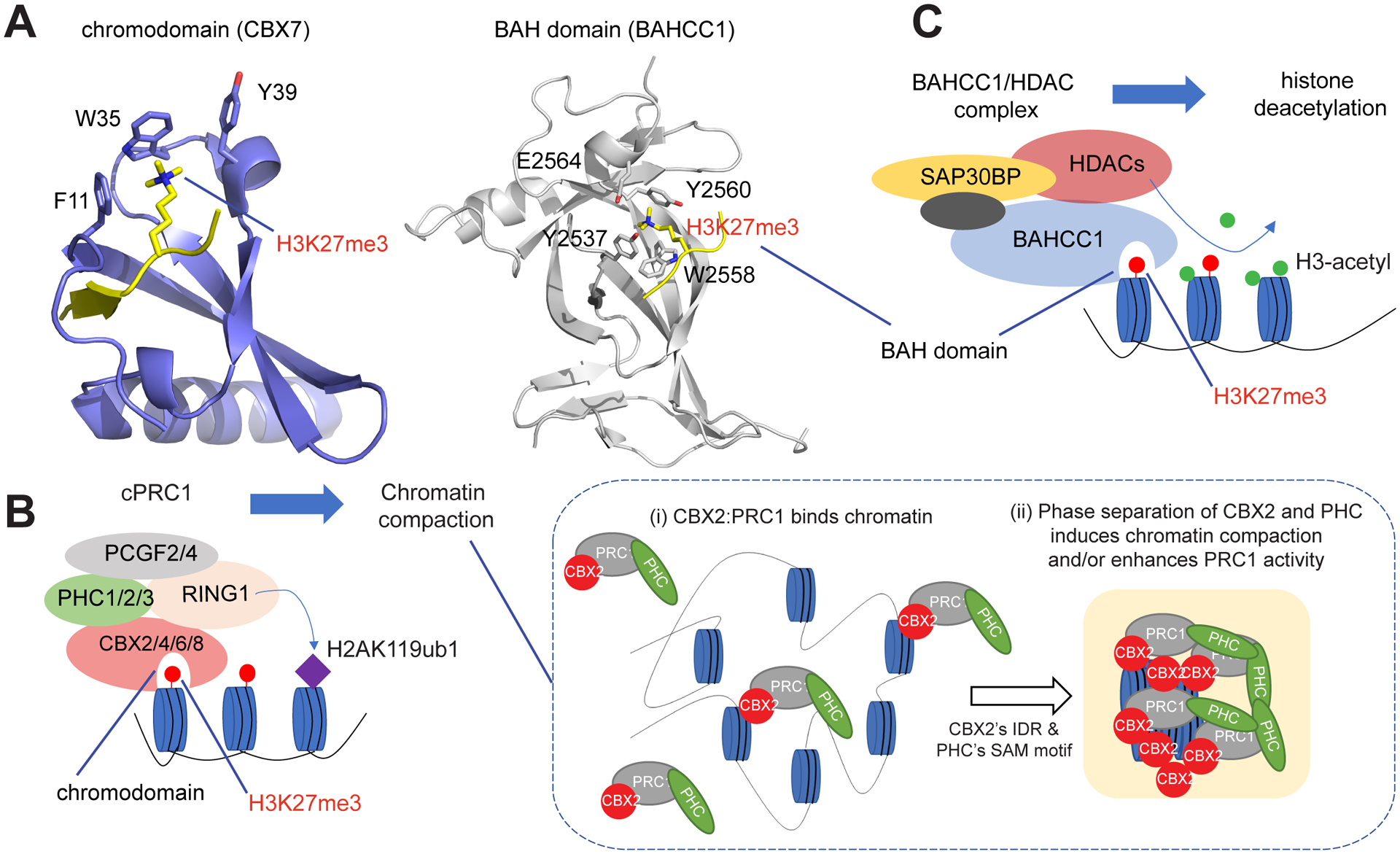
(A) Structure showing recognition of H3K27me3 by the chromodomain of CBX7 (left) or by the BAH domain of BAHCC1 (right); the key H3K27me3 reading cage residues are labeled. H3 peptide is shown in yellow. (B) Scheme illustrating that, cPRC1 reads H3K27me3 via the chromodomain of its CBX subunit, and then mediates deposition of histone 2A ubiquitinated on Lys119 (H2AK119ub1) and chromatin compaction (left). For the latter (right), intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) that are present in CBX2/4/6/8 (but not in CBX7), as well as the SAM domain of the PHC subunit, both phase-separate, inducing cPRC1 condensation to enhance chromatin compaction/folding. (C) A model that specific readout of H3K27me3 by a conserved BAH module in BAHCC1 leads to recruitment of BAHCC1, HDAC1/2, and corepressors to deacetylate local histones and silence H3K27me3-demarcated genes.
