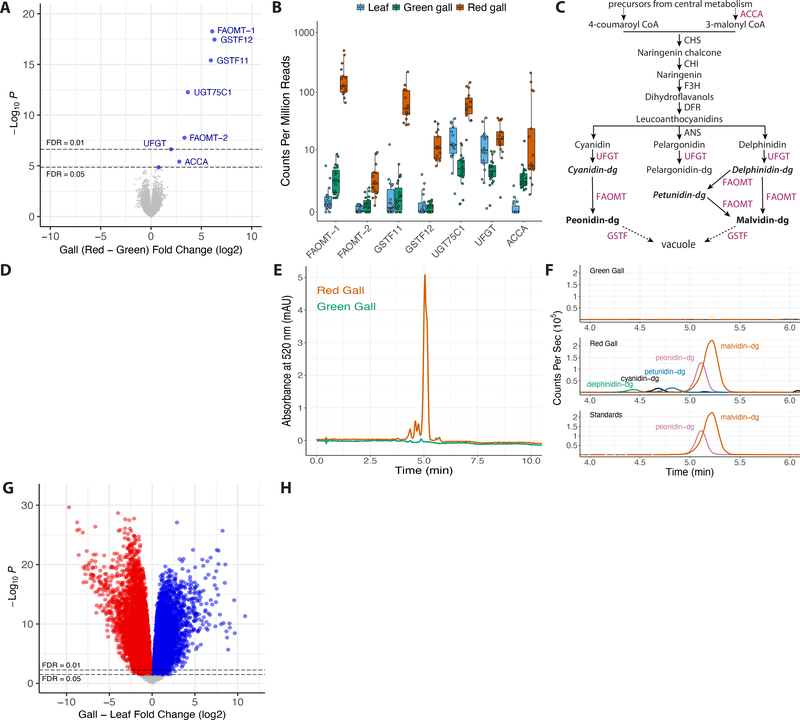
Figure 4. Genome-wide differential expression analysis of H. virginiana red versus green galls and galls versus leaves.
(A) Genome-wide differential expression analysis of H. virginiana transcripts isolated from galls made by fundatrices heterozygous for dgcRed/dgcGreen (Red; N = 17) versus homozygous for dgcGreen (Green; N = 23) illustrated as a volcano plot. Only eight genes are differentially expressed at FDR < 0.05, and all are overexpressed in red galls. The seven most strongly differentially expressed genes encode anthocyanin biosynthetic enzymes (FAOMT-1 = g23591; FAOMT-2 = g7147; GSTF11 = g134919; GSTF12 = g109682; UGT75C1 = g14194; UFGT = g22774; ACCA = g97071).
(B) Expression levels, in counts per million reads, of the seven anthocyanin biosynthetic genes overexpressed in red galls, in green (green) and red (red) galls and ungalled leaves (blue). Each data point within each gene is from a separate genome-wide RNA-seq sample.
(C) Simplified diagram of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway. Enzyme classes upregulated in red galls are shown in purple font. The two terminal anthocyanins that generate the red color in galls, peonidin-3,5-diglucoside and malvidin-3,5-diglucoside, are shown in bold font, and three precursor molecules found in red galls are shown in bold italic font. Anthocyanin names are abbreviated (dg = 3,5-diglucoside).
(D) Photos of cross-sections of green (top left) and red (top right) and the pigments extracted from green and red galls (below).
(E) UHPLC-DAD chromatograms at 520 nm of extract from red (red line) and green (green line) galls.
(F) Overlaid UHPLC-MS chromatograms of green (top) and red (middle) gall extracts and authentic standards (bottom). Each pigment is indicated with a different color: green = delphinidin-3,5-diglucoside (m/z = 627.1551); black = cyanidin-3,5-diglucoside (m/z = 611.1602); blue = petunidin-3,5-diglucoside (m/z = 641.1709); purple = peonidin-3,5-diglucoside (m/z = 625.1768); and red = malvidin-3,5-diglucoside (m/z = 655.1870). Anthocyanin names are abbreviated (dg = 3,5-diglucoside). Peonidin-3,5-diglucoside and malvidin-3,5-diglucoside together account for 87% of pigment detected in red galls.
(G) Genome-wide differential expression analysis of H. virginiana transcripts isolated from galls (N = 36) versus leaves (N = 17). Approximately 60% of expressed genes are differentially expressed between gall and leaf tissue at FDR < 0.05.
(H) Gene ontology analysis of GO terms down (left) and up-regulated (right) in galls, presented as volcano plots. Genes involved in cell division and morphogenesis were strongly upregulated in galls and genes involved in photosynthesis were strongly down-regulated in galls.
See also Figure S3.