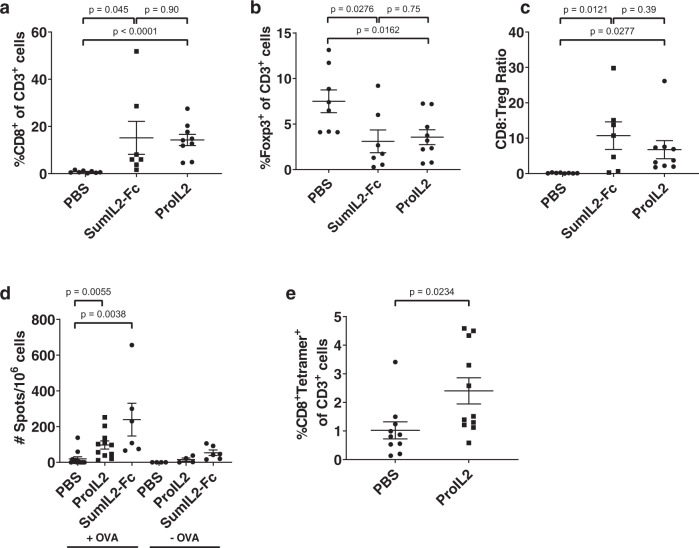
Fig. 5. In vivo flow cytometry analysis of ProIL2.
a–c B16 s.c. tumor-bearing mice were injected i.p. with PBS, SumIL2-Fc or ProIL2 (300 pmol) two times on days 9 and 12 post tumor inoculation. 48 h after the last treatment, mice were euthanized and tumors were extracted, digested in collagenase/DNAse, and resuspended as single cells. Flow cytometry was used to quantify the amount of CD8 T cells, amount of Tregs, and CD8:Treg ratio in each respective group (n = 2 experiments, total 8 individual mice for PBS treatment group, 7 for SumIL2-Fc, 9 for ProIL2). d B16-OVA s.c. tumor-bearing mice were injected i.p. with PBS or ProIL2 (300 pmol) one time on day 9 post tumor inoculation. 5 days after treatment, draining lymph nodes were collected, IFNγ ELISPOT analysis was performed and spots were quantified (n = 2 experiments, total 12 individual mice for PBS/OVA group, 11 for ProIL2/OVA, 6 for SumIL2-Fc/OVA, 4 for PBS/no OVA, 4 for ProIL2/no OVA, 6 for SumIL2-Fc/no OVA). e B16-OVA s.c. tumor-bearing mice were injected i.p. with PBS or ProIL2 (300 pmol) one time on day 9 post tumor inoculation. 5 days after treatment, mice were euthanized and tumors were extracted, digested in collagenase/DNAse, and resuspended as single cells. Flow cytometry was used to quantify the amount of OVA-tetramer CD8 T cells (n = 3 experiments, total 10 individual mice for PBS treatment group, 11 for ProIL2). Data represent mean ± s.e.m. Student’s t tests were performed to calculate p values. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.