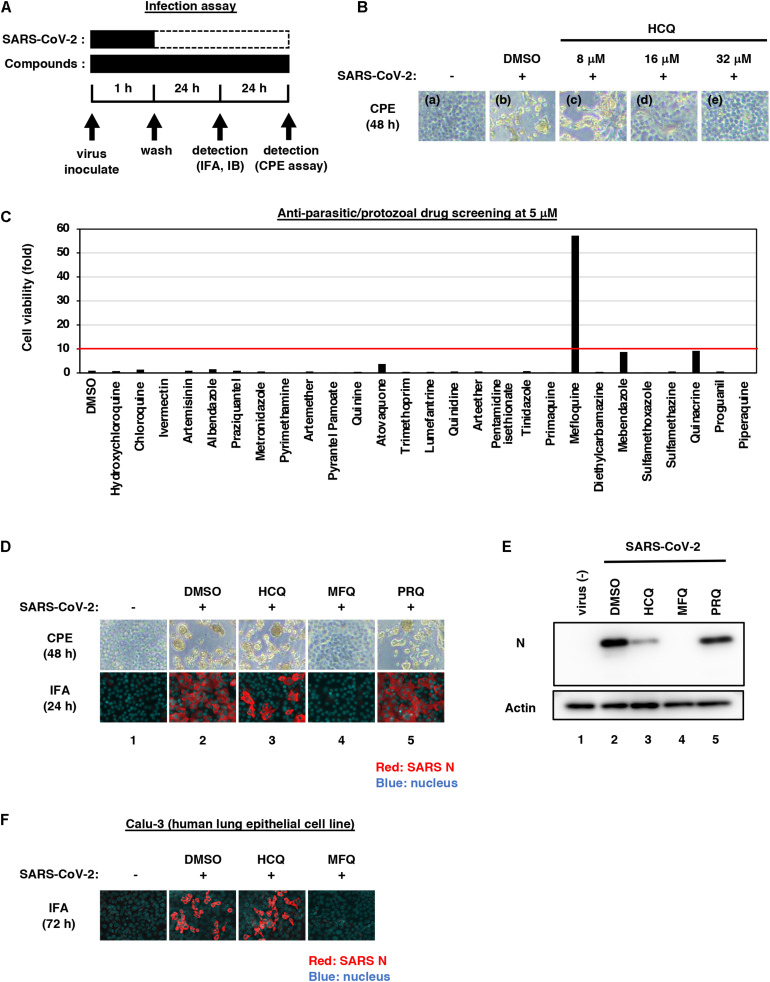
FIGURE 1.
Mefloquine (MFQ) inhibits Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) propagation. (A) Schematic representation of the SARS-CoV-2 infection assay. VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells were inoculated with SARS-CoV-2 (Wk-521 strain) at an MOI of 0.001 for 1 h. After removing the unbound virus, cells were cultured for 24 h to detect virus-encoding N protein by immunofluorescence assay (IFA) and immunoblot (IB) or to detect viral RNA in the culture supernatant by RT-qPCR, or for 48 h to observe virus-induced cytopathic effect (CPE). Compounds were treated given throughout the assay. (B) Dose dependency of Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) on CPE suppression. VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells were inoculated with the virus for 1 h. Removing the unbound virus, cells were cultured with a medium containing the indicated compounds for 48 h. CPE was observed by microscopy. (C) Screening of anti-parasitic/protozoal drugs in the cell-based infection assay. Compounds were administrated at 5 μM, at which hydroxychloroquine showed little effect on CPE. The viability of infected cells was quantified via a high content imaging analyzer by setting the value for the sample treated with DMSO solvent as 1. MFQ showed more than 57-fold higher cell viability than DMSO controls. (D,E) SARS-CoV-2-induced CPE and viral N protein expression upon compound treatments [DMSO at 0.08%; hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), mefloquine (MFQ), and primaquine (PRQ) at 8 μM]. Red and blue signals of merged images indicate viral N protein and nucleus, respectively (D, lower). Viral N protein and actin, an internal control, were detected by immunoblot (E). (F) The anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of the indicated compounds in Calu-3 cells, a human lung epithelial cell-derived line.