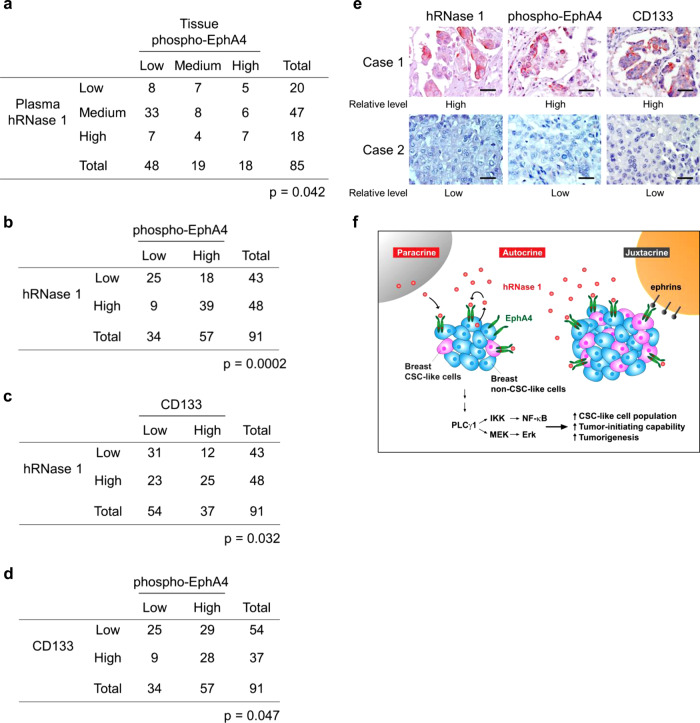
Fig. 7. Pathological relevance of hRNase 1 expression, EphA4 activation, and CD133 in breast cancer.
a Quantification for the correlation between tissue phospho-EphA4-Y779 and plasma hRNase 1 in the paired breast cancer patients. Chi-squared test. b–d Quantification of IHC staining for the correlation between hRNase 1 and phospho-EphA4-Y779 (b), hRNase 1 and CD133 (c), and CD133 and phospho-EphA4-Y779 (d) by human breast TMA analysis (Pantomics Inc., #BRC1021). Fisher’s exact test. e Two representative cases of IHC staining for (b–d). The experiment was performed an additional time with similar results. Bar, 50 μm. f A proposed model of hRNase 1 as a secretory ligand of EphA4 to positively regulate breast tumor initiation. In brief, elevated levels of serum hRNase 1 induces its binding to EphA4 and triggers EphA4 signaling (red stars) in breast tumor cells in an autocrine/paracrine manner, which in turn promotes breast tumor initiation via the IKK/NF-κB and MEK/Erk activating pathways. Such EphA4 activation and CSC-like state triggered by hRNase 1 may be sustained in conjunction with juxtacrine signaling via the classical membrane-bound EphA4 ligands, ephrins. Artwork by H-H.L., Y-N.W., and M-C.H.