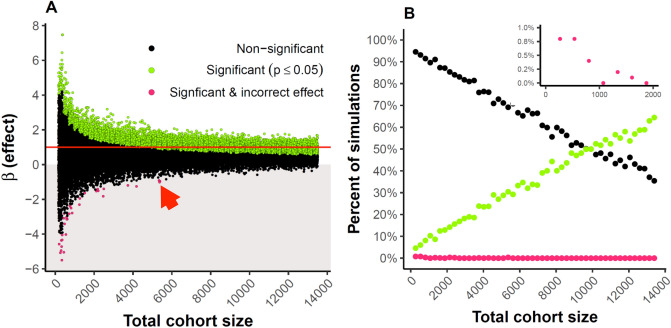
Figure 6.
(A) We conducted 1000 down-sample linear regression models of the MindCrowd cohort between the ages of 18 and 85 years for the interaction effect (β, y axis) of sex × smoking on paired associate learning (PAL) for each indicated total sample size (x axis). For each analysis, we had an equal amount of smokers and non-smokers and women and men. The horizontal red line indicates the effect size estimated by the total study sample. Green filled circles indicate an individual down-sampled comparison that resulted in a statistically significant association (p < 0.05), black dots are non-significant comparisons. Red arrow highlights that at samples sizes approximating 5000 one could potentially produce a significant beta value with the opposite sign from the largest sampled model. (B) is the same data displayed to easily see the positive relationship between significant betas and sample size.