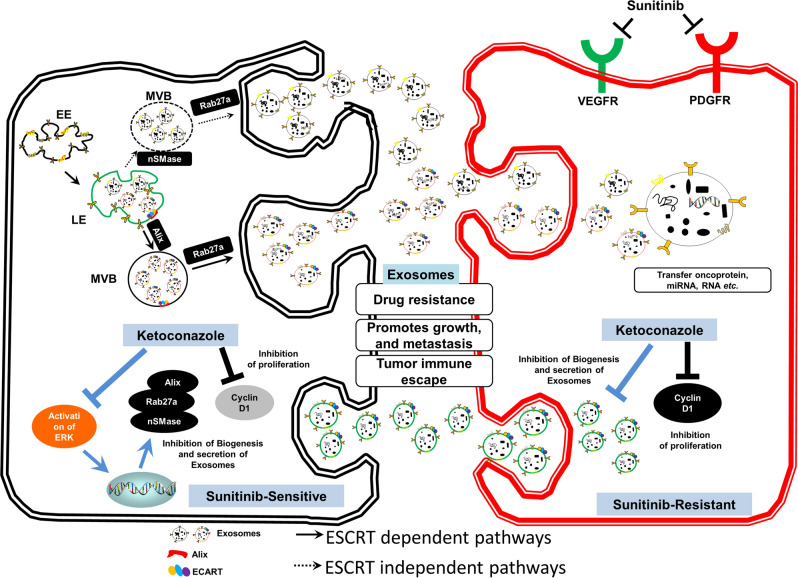
Figure 6.
Illustrative diagram for exosome-mediated transfer of therapeutic resistance in the RCC microenvironment by the clinically approved KTZ. Exosome act as intercellular messengers that give the ability to communicate between both cells of the same type and other cell types. The exosome cargoes contain nucleic acids (miRNAs, DNAs, and RNAs), proteins (cytoplasmic proteins, tetraspanins, and membrane receptors), and lipids (ceramides, and cholesterol). The exosomes secreted from cancer cells can affect the local tumor microenvironment, alter the extracellular matrix, and enhance the drug resistance, cancer cell growth, metastasis, and immune escape. The initial steps of this process are usually modulated by the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) dependent or ESCRT independent pathway, and then the mechanisms involved in the release of exosomes are also regulated by other protein families, such as Rab GTPases such as Rab27a and Rab27b. The inhibition of ERK1/2 pathway by KTZ leads to transcriptional downregulation of Alix, nSMase, and Rab27a. A inhibition of exosome biogenesis and secretion relative proteins, and the inhibition of cyclin D1 by KTZ are decreased the tumor growth of RCC as well as sunitinib resistant cancer cells. (EE) early endosome; (LE), late endosome; (MVB), multivesicular bodies; (ESCRT), endosomal sorting complex required for transport.