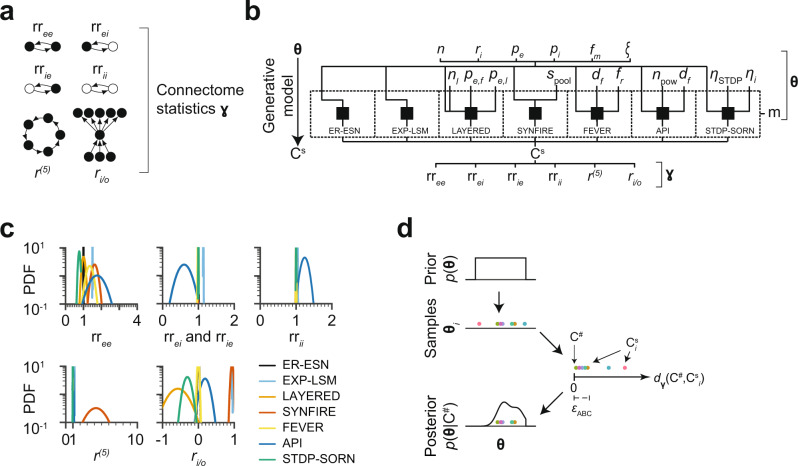
Fig. 3. Connectome statistics and generative models for approximate Bayesian inference.
a Connectome statistics used for model distinction: relative excitatory-excitatory reciprocity , relative excitatory-inhibitory reciprocity , relative inhibitory-excitatory reciprocity , relative inhibitory-inhibitory reciprocity , relative cycles of length 5, , and in-out degree correlation of excitatory neurons b Generative model for Bayesian inference: shared set of parameters (top: number of neurons , fraction of inhibitory neurons , excitatory connectivity , inhibitory connectivity , fractional connectome measurement , noise ) and model-specific parameters (middle: model choice , number of layers , excitatory forward connectivity , excitatory lateral connectivity , pool size , STDP learning rate , intrinsic learning rate , feature space dimension , feverization ratio , selectivity , see Supplementary Fig. 4), generated sampled connectome Cs described by the summary statistics . c Gaussian fits of probability density functions (PDFs) of the connectome statistics (a) for all models (see Fig. 1b). d Sketch of ABC-SMC procedure: given a measured connectome , parameters (colored dots) are sampled from the prior . Each generates a connectome that has a certain distance to in the space defined by the connectome statistics (a). If this distance is below a threshold , the associated parameters are added as mass to the posterior distribution , and are rejected otherwise.