Figure 1 .
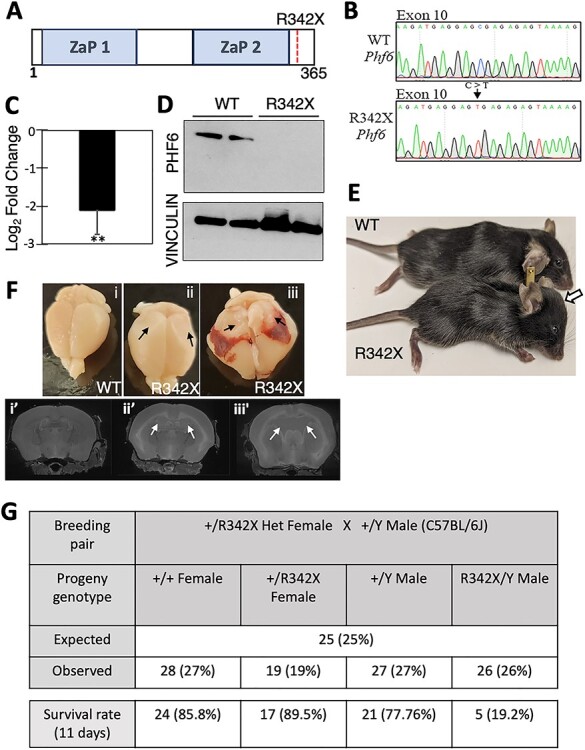
Generation of the R342X mice. (A) Schematic diagram of the PHF6 protein highlighting the location of the ZaP domains and the R342X nonsense mutation. (B) DNA sequence traces from the WT and R342X mESCs showing the engineered C to T transition at nucleotide 1024 within exon 10 of the Phf6 gene. (C) Plot of RT-qPCR log2-fold change of Phf6 from the R342X mESCs relative to WT mESCs. **, P < 0.01. (D) Phf6 immunoblot of extracts from WT or R342X mESCs. Vinculin was used as a loading control. (E) Photo of P40 WT and R342X mice on a C57BL/6 background. Arrow indicates dome-shaped head in mutant animal. (F) Dissected brains (top) or MRI scans (bottom) from WT (i) or R342X mice with mild (ii) or severe (iii) hydrocephaly at P100. Black arrows indicate collapsed cortical tissue due to loss of CSF from the enlarged ventricles which are indicated by white arrows in the bottom panel. (G) R342X male mice (C57BL/6) were born at normal Mendelian ratios but only had a 20% survival rate by P11.
