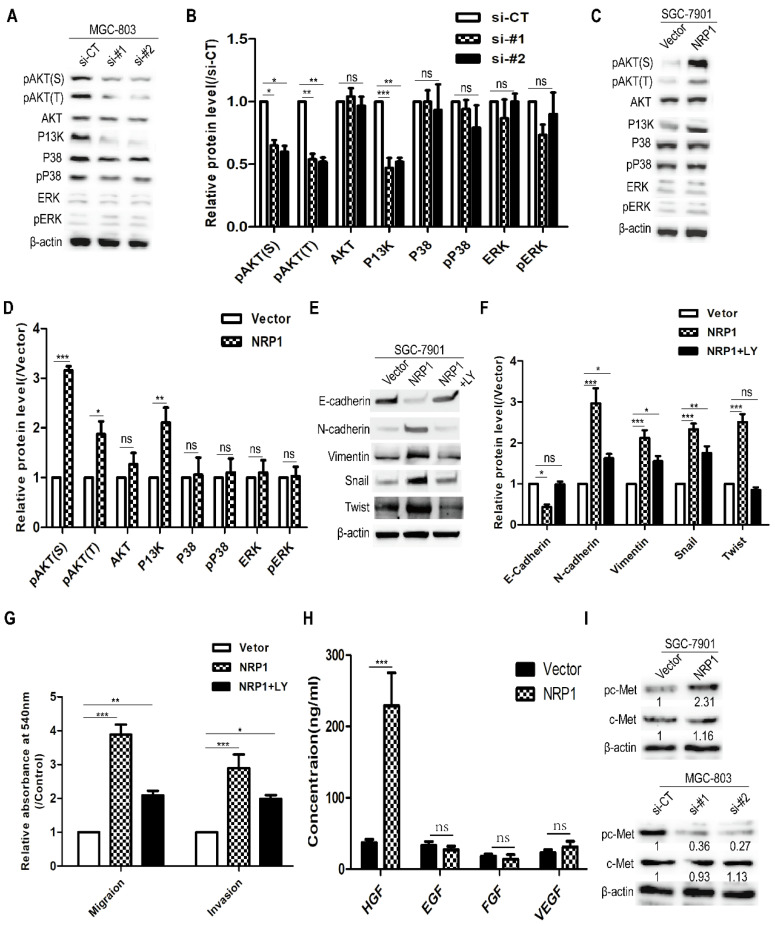
Figure 5.
NRP1 induced EMT to promote the migration and invasion of GC cells by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. (A-B) The effect of highly NRP1 expression on Akt, P38, ERK and PI3K signaling pathways was assessed by Western blotting. (C-D) The effect of NRP1 knockdown on Akt, P38, ERK and PI3K signaling pathways was assessed by western blotting. (E-F) SGC-7901 cells with NRP1 overexpression plasmid were treated with LY294002, and the expression of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Vimentin, Snail and Twist were detected by western-blotting. (G) SGC-7901 cells with NRP1 overexpression plasmid were treated with LY294002 and applied to transwell analysis. (H) The levels of several extracellular growth factors (HGF, EGF, FGF, and VEGF) in the cell culture supernatants were measured by ELISA. (I) c-Met protein levels in GC cells transfected with siNRP1 and NRP1 overexpression plasmid was detected by Western-blotting. Data were mean ± SD. These data were obtained from three independent experiments. GC, gastric cancer; NRP1, Neuropilin-1; LY294002, a PI3K/Akt signaling pathway inhibitor; *, P< 0.05; **, P< 0.01; ***, P< 0.001; ns, no significant.