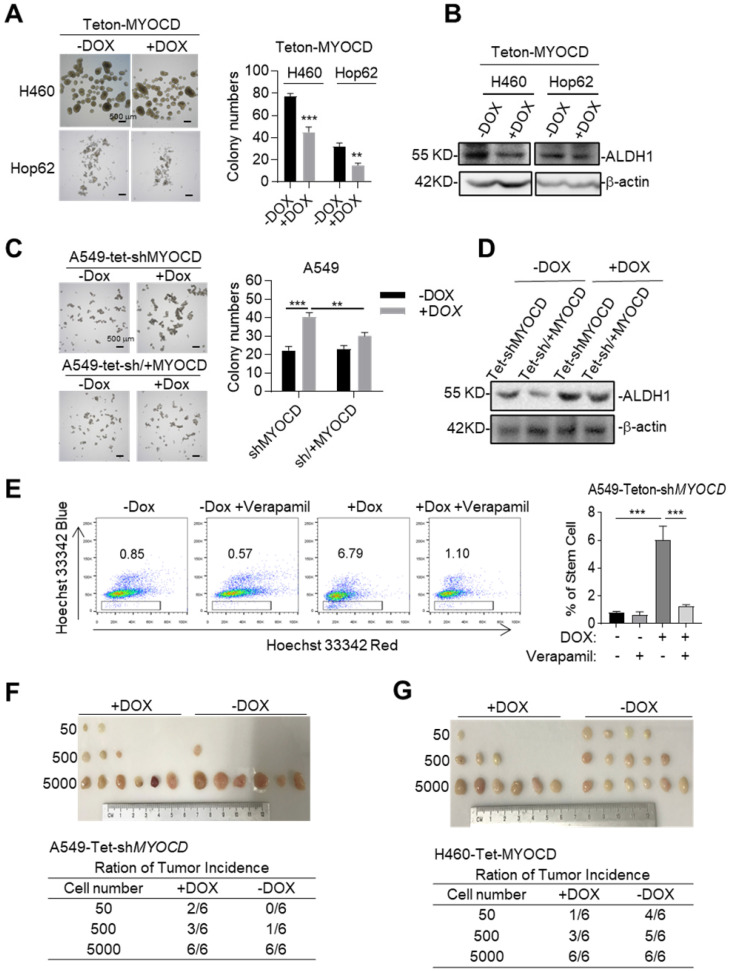
Figure 2.
MYOCD inhibits stemness of lung cancer cells. (A) MYOCD inhibited sphere formation ability of H460 and Hop62 cells. H460-Teton-MYOCD and Hop62-Teton-MYOCD cells were treated with DOX or not treated for around 2 weeks before quantification. Representative images of sphere assay (left panel), statistics of sphere formation of colony numbers (right panel). (B) MYOCD reduced ALDH1 expression in H460 and Hop62 cells. H460-Teton-MYOCD and Hop62-Teton-MYOCD cells were not treated or treated with DOX for 48 hours. The whole lysates were analyzed by IB with the indicated antibodies. (C) MYOCD knockdown promoted sphere formation ability of A549 cells. Representative images of sphere assay (left), statistics of sphere formation of colony numbers (right). (D) MYOCD inactivation increased ALDH1 expression. (E) MYOCD inactivation increased frequency of side population cells in A549 cells. Side Population was analyzed through uptake of Hoechst33342 red with or without the presence of verapamil. Representative images of FACS analysis (left) and statistics of stem cells (right). (F-G) Tumor incidence was measured by Limiting Dilution Assays (LDA). A549-Teton-shMYOCD cells (F) or H460-Teton-MYOCD (G) were subcutaneously injected 6-week-old female BALB/c nude mice, followed by treatment with DOX or control diet for 21 days before sacrificed mice. Images of tumor (upper panel), number of mice with a positive response (response = tumor >100 mm3) at 21 days post-injection (lower panel).