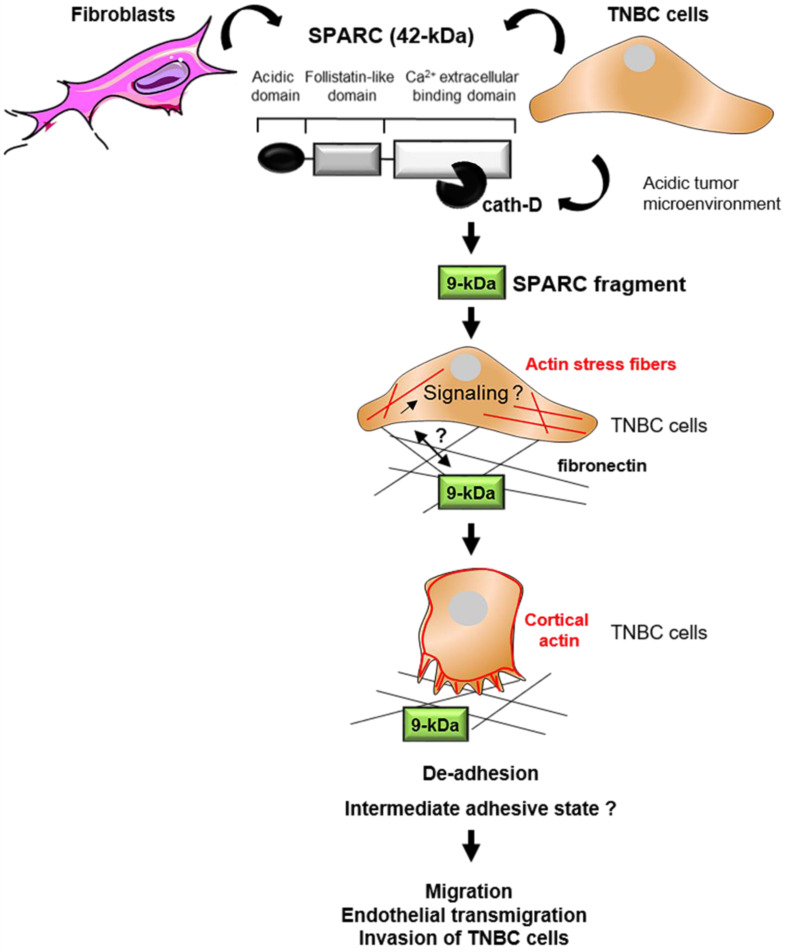
Figure 9.
Model of the pro-tumor effect on TNBC cells of the 9-kDa C-terminal SPARC released by cath-D cleavage. TNBC-secreted cath-D triggers limited proteolysis of SPARC at the acidic pH of the tumor microenvironment. Among the SPARC fragments cleaved by cath-D, the 9-kDa C-terminal SPARC fragment inhibits TNBC cell adhesion and spreading. This might lead to an intermediate adhesive state, and stimulate TNBC cell migration, endothelial transmigration and invasion.