Figure 3.
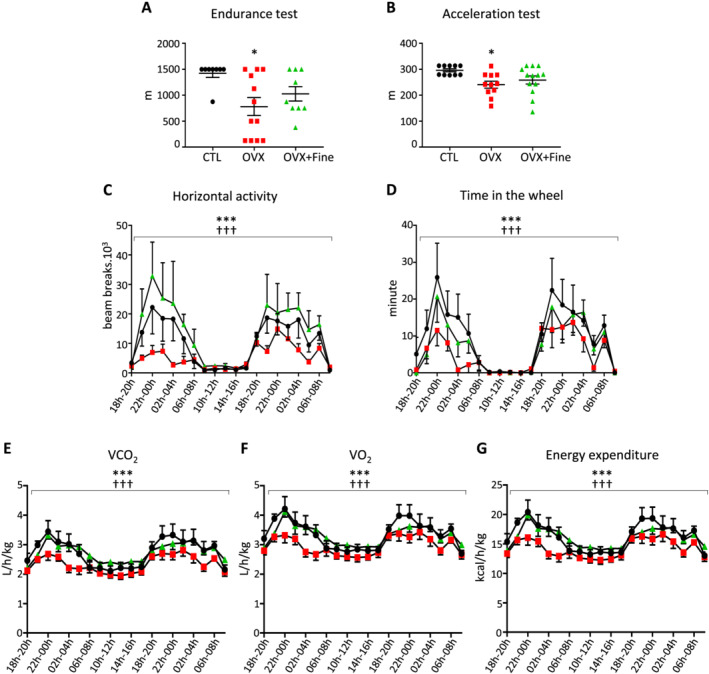
Finerenone treatment improved ovariectomy‐induced decreased ability to exercise. Assessments in control mice (CTL, black circles) and in mice after 4 months of ovariectomy (OVX, red squares) without or with 1 month finerenone treatment (OVX + Fine, green triangles). (A) Run distance during an endurance (n = 8, 12, 9) or (B) an acceleration (n = 10, 11, 13) test at race. (C–G) Spontaneous activity (n = 8, 8, 8), each x‐axis point being the integration per 2 h interval according to a 24 h clock, in cages with free access to an exercise wheel and indirect calorimetry measurements: (C) spontaneous horizontal activity, (D) time spent in the wheel, (E) VO2, (F) VCO2, and (G) energy expenditure. Data are mean ± standard error of the mean. Statistics: (A, B) one‐way ANOVA plus Tukey and (C–G) multivariate analysis, *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. CTL; †† P < 0.01 and ††† P < 0.001 vs. OVX.
