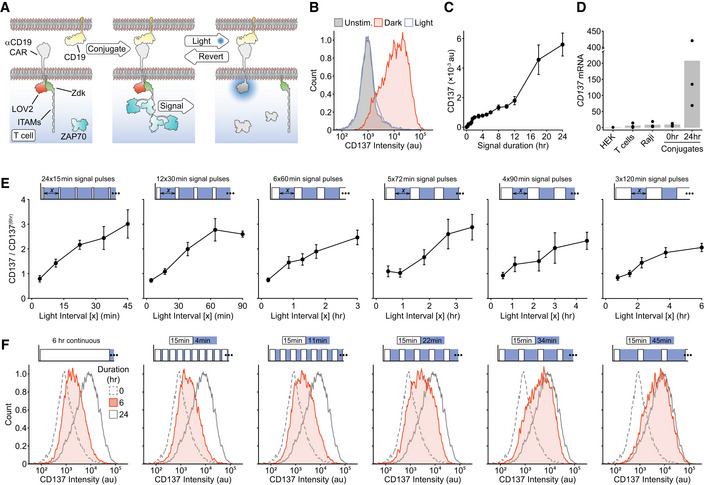
Schematic showing the anti‐CD19 OptoCAR engineered to be light‐responsive. Binding of the OptoCARCD19 expressed in T cells to CD19‐expressing B cells drives signaling through an equivalent intracellular sequence used in the OptoCAR, where illumination with blue light causes the reversible disruption of receptor signaling.
Stimulating primary CD4+ T cells expressing OptoCARCD19 over 24 h in the dark drives expression of CD137 (4‐1BB), a robust activation marker. Continuous illumination completely abolishes this to CD137 levels equivalent to unstimulated T cells.
Plot of geometric mean of CD137 expression when the length of an individual signaling pulse is varied. Single pulse ranged from 0 to 24 h, with sample illumination initiated at the end of the pulse and CD137 expression measured for all samples 24 h after initiation of signaling. Bars show mean ± SEM of biological replicates (n = 4).
The cRQ values from RT‐qPCR of indicated cells. Total RNA was extracted and CD137 mRNA levels measured relative to that from HEK293T cells. Conjugated OptoCARCD19‐T cells were also assayed either before or after 24 h stimulation in the dark state. Individual values from three biological replicates are shown, with mean depicted by bar plot.
Series of experiments showing how CD137 expression is modulated by pulsatile trains of signaling in primary CD4+ T cells activated through OptoCARCD19. A combined signaling period of 6 h was broken into pulses ranging from 15 min to 2 h and the refractory period between these pulses varied (x‐axis), shown in the schematic above each plot. Geometric mean of CD137 intensity is shown plotted as a function of inter‐pulse interval, scaled to continuous 6‐h output. Bars show mean ± SEM (n = 5).
Representative dataset from (E), demonstrating how pulsatile stimulation of OptoCARCD19‐T cells drives more efficient activation. Dotted and gray histograms show CD137 expression in resting cells and 24‐h activation, respectively. The filled histogram shows either a continuous 6‐h stimulation (left) or cumulative pulsed signals over 24 h driving substantially more potent activation.