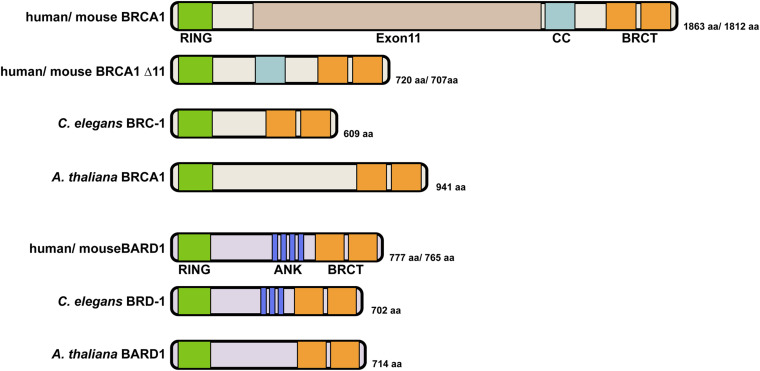
FIGURE 1.
Domain structure of BRCA1 and BARD1 proteins. Human BRCA1 contains an N-terminal RING domain, an unstructured central region encoded by the large exon11 followed by a coiled coil (CC) domain and two BRCA1 C-terminal (BRCT) repeats. Both human and mouse express an alternatively spliced variant BRCA1Δ11 that contains the N-terminal RING domain and C-terminal BRCT repeats but lacks the unstructured central region (Thakur et al., 1997; Huber et al., 2001). This truncated protein is expressed in the hypomorphic Brca1Δ11/Δ11 mouse. C. elegans BRC-1 is structurally similar to the BRCA1Δ11 splicing variant with the presence of an N-terminal RING domain and two BRCT repeats at its C terminus. A. thaliana encodes a similarly structured BRCA1 ortholog that has a N-terminal RING and two C-terminal BRCT repeats. Human BARD1 and C. elegans BRD-1 are similar in size and domain structure, containing an N-terminal RING domain, ankyrin repeats in the middle and two C-terminal BRCT repeats. A. thaliana BARD-1 has a similar domain structure but appears to lack ankyrin repeats, which were not predicted by sequence alignment. BRCA1 interacts with BARD1 through their RING domains to form a heterodimer with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity.