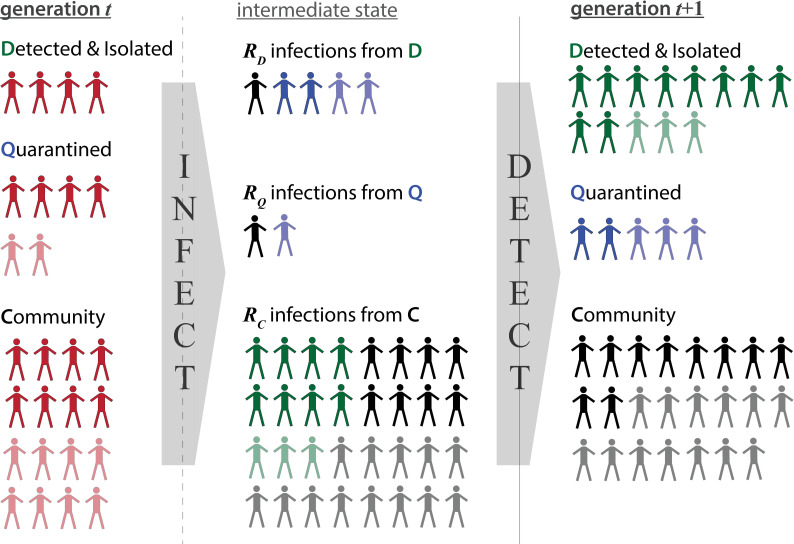
Fig 1.
Conceptual representation of the model algorithm, where infections in generation t (left column) infect new individuals according to RD, RQ, and RC reproductive numbers that populate the INFECT matrix (center column). These newly propagated infections are then distributed into D, Q, and C compartments in generation t+1 (right column) according to the various detection transition probabilities specified in the DETECT matrix (colors of center column). Symptomatic individuals (darker shading) may be more likely to be detected than asymptomatic individuals (lighter shading).