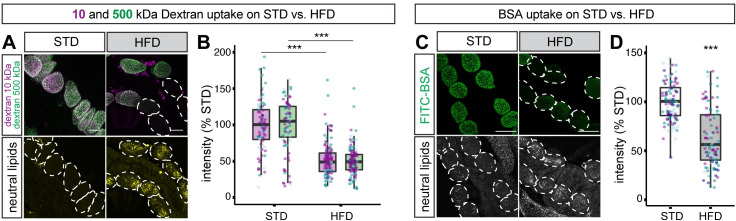
Fig 2. HFD decreases nephrocyte uptake of dextran and albumin.
(A, B) Dextran uptake assay. (A) Nephrocytes from STD and HFD larvae shown after ex vivo incubation with labelled 10-kDa (magenta) and 500-kDa (green) dextran. Bottom row shows same field of view with lipid droplets revealed with a neutral lipid stain (LipidTOX). Dashed outlines indicate the positions of all nephrocytes in the bottom row, but only those that show weak dextran uptake in the top row. (B) Graph shows that uptake of both 10-kDa (magenta) and 500-kDa (green) dextran is significantly higher on STD than on HFD (p < 0.0005). Scale bar = 30 μm. (C, D) Albumin uptake assay. (C) Nephrocytes from STD and HFD larvae shown after ex vivo incubation with labelled bovine serum albumin (FITC-BSA). Bottom row shows same field of view with lipid droplets revealed with a neutral lipid stain (LipidTOX). Dashed outlines indicate the positions of all nephrocytes in the bottom row, but only those that show weak albumin uptake in the top row. (D) Graph shows that uptake of albumin is significantly higher on STD than HFD (p < 0.0005). Scale bar = 50 μm. See S1 Data for details of p-values and the type of statistical model used for all graphs in this study. S2 Data provides the source data used for all graphs and statistical analyses. HFD, high-fat diet; STD, standard diet.