Fig. 4. Vangl-p97/VCP direct interaction recruits KBTBD7 for Vangl ubiquitination.
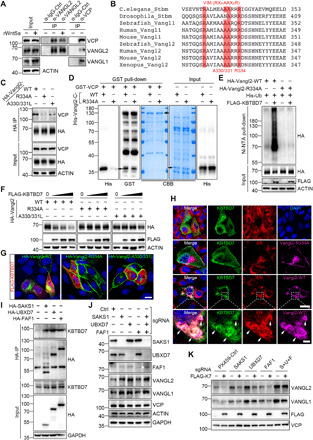
(A) Endogenous interaction between Vangl2 and VCP in HEK293T cells. rWnt5a, recombinant Wnt5a (200 ng/ml, 2 hours). (B) Sequence alignment identified a well-defined VCP-interacting motif (VIM) RX5AAX2R that is highly conserved across multiple species in both Vangl1 and Vangl2. (C) Mutations in Vangl2 VIM (R334A or A330/331L) nearly abrogated its interaction with p97/VCP. (D) VCP directly binds to Vangl2 via VIM. GST-fused VCP and His-fused C-terminal (amino acids 254 to 521) WT or VIM mutant (R334A) Vangl2 were purified, coincubated, and then subjected to GST pull-down. (E) KBTBD7 failed to induce the ubiquitination of VIM mutant (R334A) Vangl2. (F) VIM mutant Vangl2 (R334A or A330/331L) is resistant to the KBTBD7-induced degradation. HEK293T cells were transfected with an increasing dose (0, 250, 500, and 1000 ng) of KBTBD7. (G) KBTBD7 (red) failed to abolish the membrane localization of VIM mutant Vangl2 (R334A or A330/331L, green) in MDCK cells. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. (H) KBTBD7 was enriched in the ER by WT Vangl2. KBTBD7 (green) was expressed with or without Vangl2 (WT or VIM mutant R334A, purple) in MDCK cells. The expression of WT but not VIM mutant Vangl2 led to an enrichment of KBTBD7 in the ER (arrows in the enlarged panel). ER was stained by ER dye (red). Scale bar, 10 μm in the top panels and 2 μm in the enlarged panel. (I) p97/VCP adaptor UBA-UBX proteins (SAKS1, UBXD7, or FAF1) bind to KBTBD7. (J) Knockdown of SAKS1 or UBXD7 by sgRNA significantly increased endogenous Vangl protein levels. (K) sgRNA-mediated knockdown of p97/VCP adaptors (SAKS1, UBXD7, and FAF1) compromised the KBTBD7-induced Vangl degradation.
