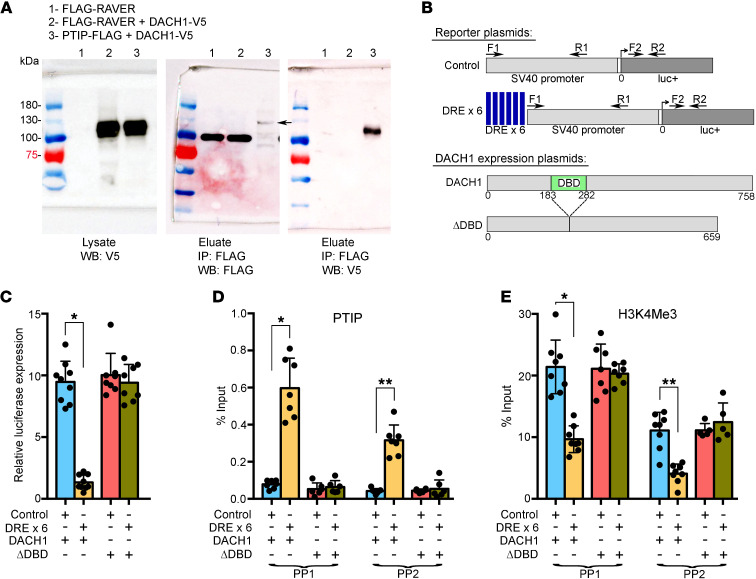
Figure 7. PTIP is recruited by DACH1 to DACH1 DNA binding sites and causes transcriptional repression and decreased H3K4Me3 levels.
(A) Co-IP was performed between PTIP-FLAG and DACH1-V5 using antibodies to their tags. FLAG-RAVER was used as a negative control protein. Indicated lysates were combined and incubated overnight with anti-FLAG antibodies bound to superparamagnetic iron–impregnated beads. A robust protein complex is present between PTIP-FLAG and DACH1-V5, but completely absent between FLAG-RAVER and DACH1-V5. Molecular weight of indicated proteins is as follows: FLAG-RAVER, 95 kDa; DACH1-V5, 105 kDa; PTIP-FLAG, 120 kDa. Protein interaction is robust despite comparatively low expression of PTIP-FLAG. Band indicated by arrow. (B) Schematic of SV40-luciferase reporter plasmids (upper) and DACH1 expression plasmids (lower). DREs were synthesized as a sextet multimer and subcloned immediately upstream of the SV40 promoter. Location of primers used for ChIP-qPCR are indicated. The DACH1 ΔDBD expression plasmid carries a deletion of its box-N domain, which mediates direct binding of DACH1 to DNA. (C) Each of the reporter plasmids was cotransfected with a DACH1 expression plasmid into 293T cells and then luciferase expression measured. Dramatic transcriptional repression was induced by the combined presence of upstream DACH1 DNA binding sites and a DACH1 protein able to bind to these sites. *P < 0.0001. (D) ChIP-qPCR was performed using an antibody specific for PTIP and primer pairs indicated in B. *P < 0.0001; **P < 0.0001. (E) ChIP-qPCR as in D, but with an H3K4Me3 antibody. *P < 0.0001; **P < 0.0001. (C–E) One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test.